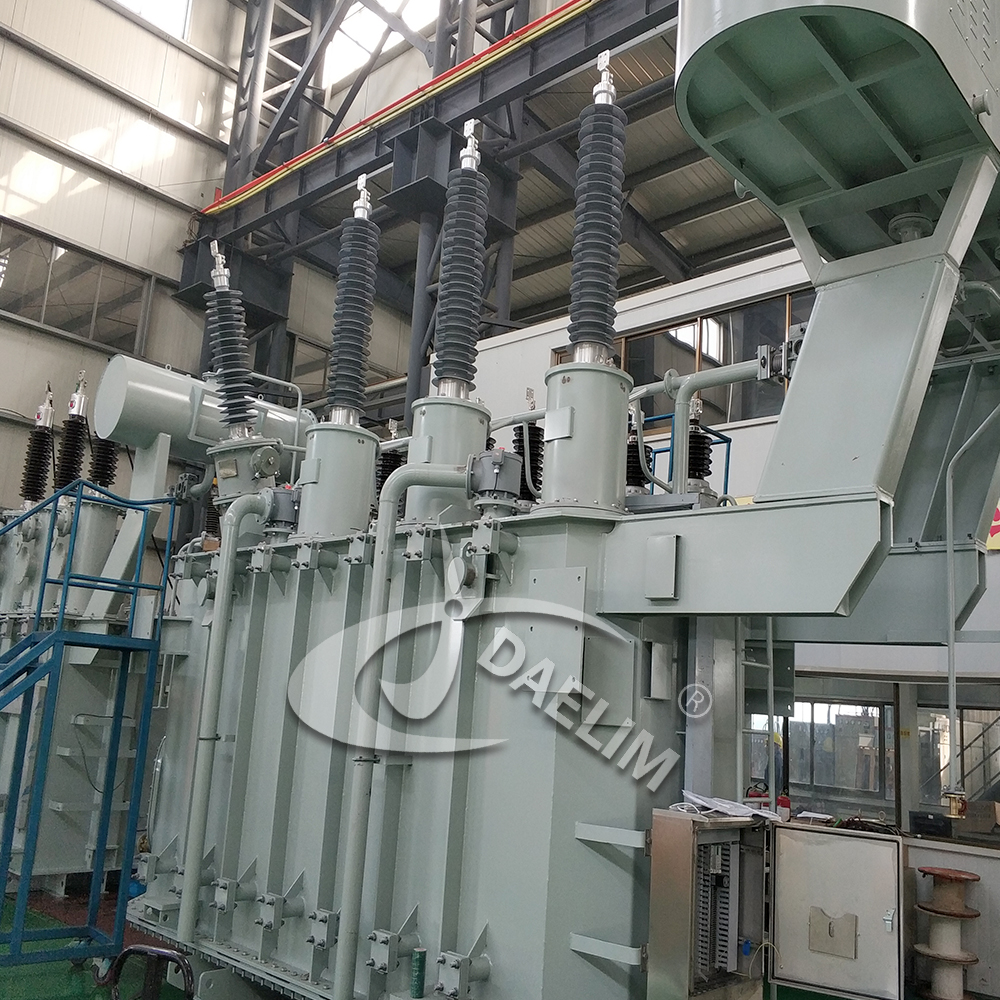
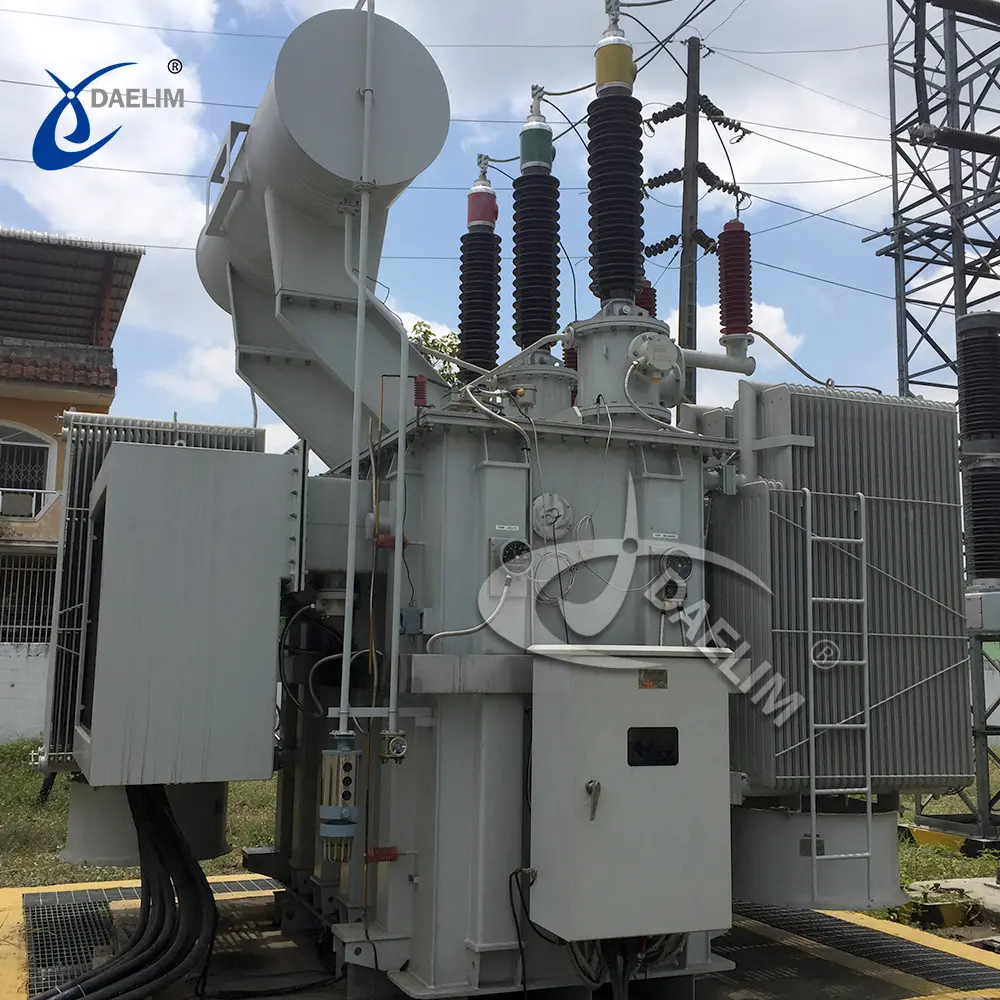
Conservator Transformers and Their Role in Power System Reliability
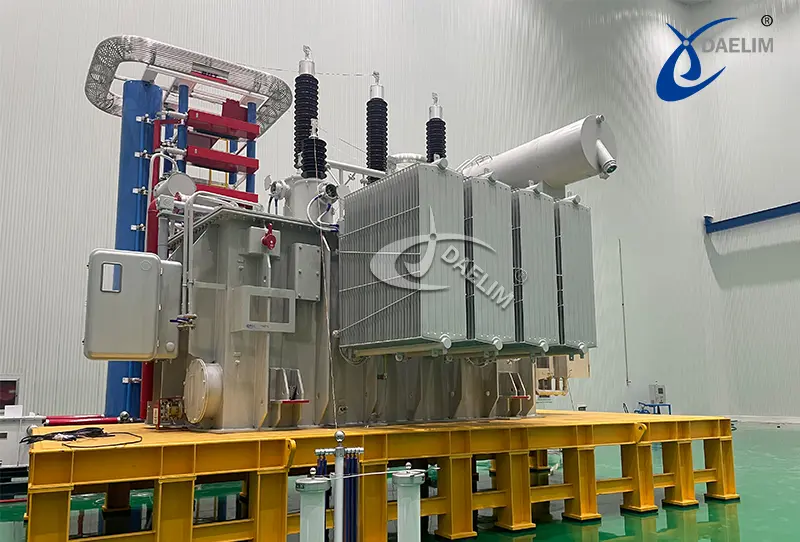

Transformers are a central element of the power system, helping to moderate and control the supply of electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. But what makes these transformers function effectively over time? The answer is a conservator transformer.
The conservator tank transformer helps maintain the oil level; hence, transformer oil helps cool and protect components within it. Without a conservator tank, the transformer might easily be affected by overheating, meaning that the system may fail, causing torque in the power supply.
Contact Daelim TransformerStructure and Components of the Oil Conservator
The oil conservator is meant to keep your transformer operating and safe. Situated directly atop the oil tank of the transformer, it is cylindrical in shape, a round tube or barrel basically. It's a beautiful shape for a reason: its purpose is to contain extra oil to allow for expansion and to compensate for the fluctuation of oil levels.
These are the major components that enable an oil conservator to perform its function:
- Oil Level Gauge: The oil level gauge gives you an indication of the amount of oil present in the conservator at any point in time. It is usually some small glass or meter, which enables you to tell that the oil level is either too high or too low. This is how you can always ensure that there's just the right amount of oil in the transformer.
- Gas Relay Connection: The gas relay connection is the linking feature between the conservator and the main oil tank. It is this movement that gives it the ability to move above or below depending on the change in temperature levels. When it is hot and expands, a part of it moves to the conservator to cool back into the major tank.
- Transformer Breather: This conservator of a transformer is a conservator tank with ventilation that keeps dust and moisture away from the oil. With such ventilation and special filters in it, the oil stays clean and free of any particles that may damage the transformer.
The other factor is the size of the conservator itself. The conservator will not be nearly the size of the main tank itself. It is normally around 10% the size of the oil tank, which is just right to store that extra oil and manage those oil level changes without taking up too much space.
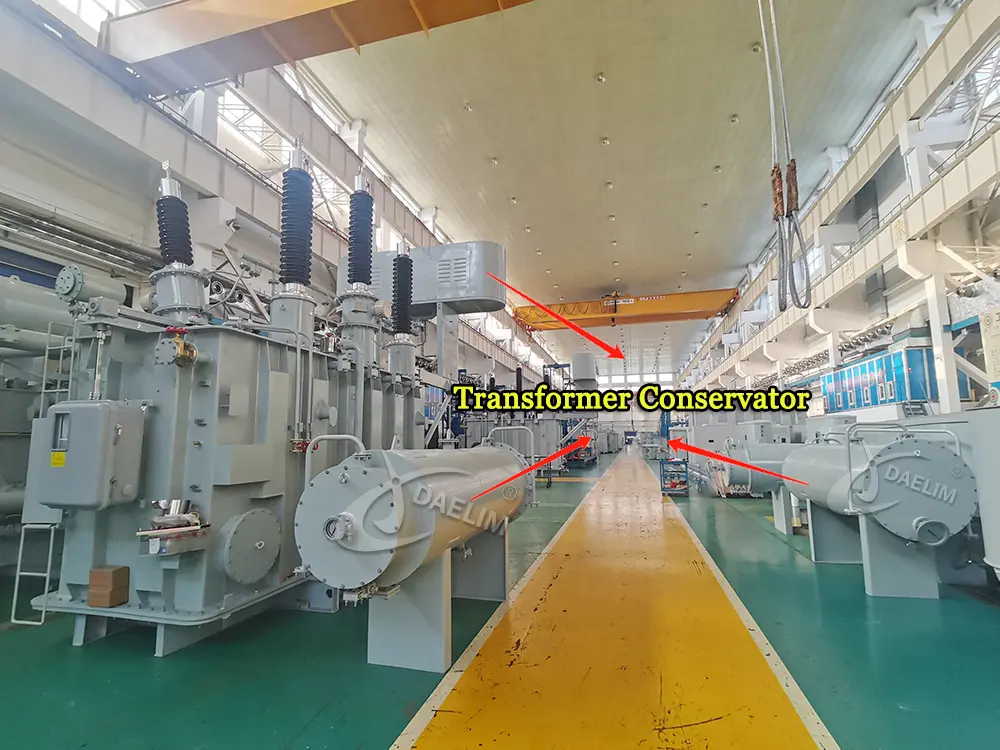

How the Conservator Tank in Transformer Helps Maintain Transformer Efficiency and Longevity
The conservator of transformer also helps transformers perform and last longer in two primary ways:
- Maintain the Right Quantity of Oil: The conservator always keeps the transformer with the right quantity of oil. This will help cool the components. Without oil, the transformer may break up and stop working, causing power problems. Overheating is thus avoided because the conservator keeps extra oil that may be needed by the transformer.
- Prevention of Oil Contamination by Air and Moisture: Air and moisture will contaminate the oil as the transformer functions. For a long time, contaminated oil may corrode a transformer. The conservator prevents contact between the oil and air and moisture. That is how the oil is kept clean, and hence the transformer is kept in a good shape.
This ensures that the transformer serves for a longer period and works effectively. The entire power transformer system, therefore, becomes reliable. If no conservator exists, the transformer might break down faster, causing a power failure and many inconveniences. Therefore, the conservator ensures that your power keeps on flowing constantly.
Role and Functions of the Transformer Conservator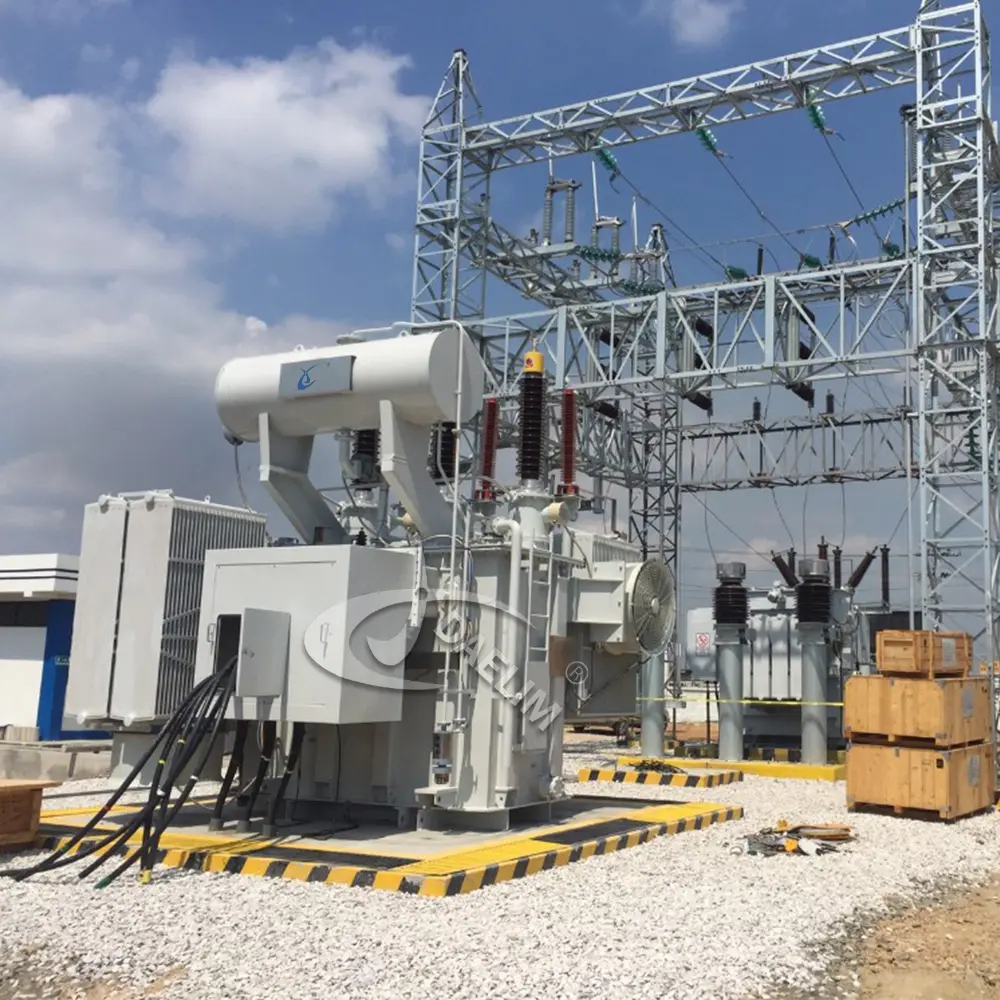
A transformer conservator is an extension storage unit for a transformer with extra oil inside. Over time, it expands and contracts when it gets too hot or too cold. The transformer conservator tank oil level is minimized by the conservator, who ensures that the transformer holds just the right amount of oil.
How the Conservator Works with Temperature Changes
When the temperature increases, then oil inside the transformer expands and occupies more space. This may cause overheating of the transformer. However, with the conservator, extra oil is held in place to prevent the transformer from overheating.
At low temperatures, the oil shrinks up and hence takes a lesser volume. Thus, the conservator allows the oil to again re-enter into the transformer in order that the level is maintained. This prevents overheating of transformers and makes them work perfectly at any temperature.
Types of Transformer Conservators
There are different types of transformer conservators. All of them have means to protect the oil from contamination and damage and also have the proper level.
There are three main types. Let's consider corrugated, capsule, and diaphragm conservators.
Corrugated Conservator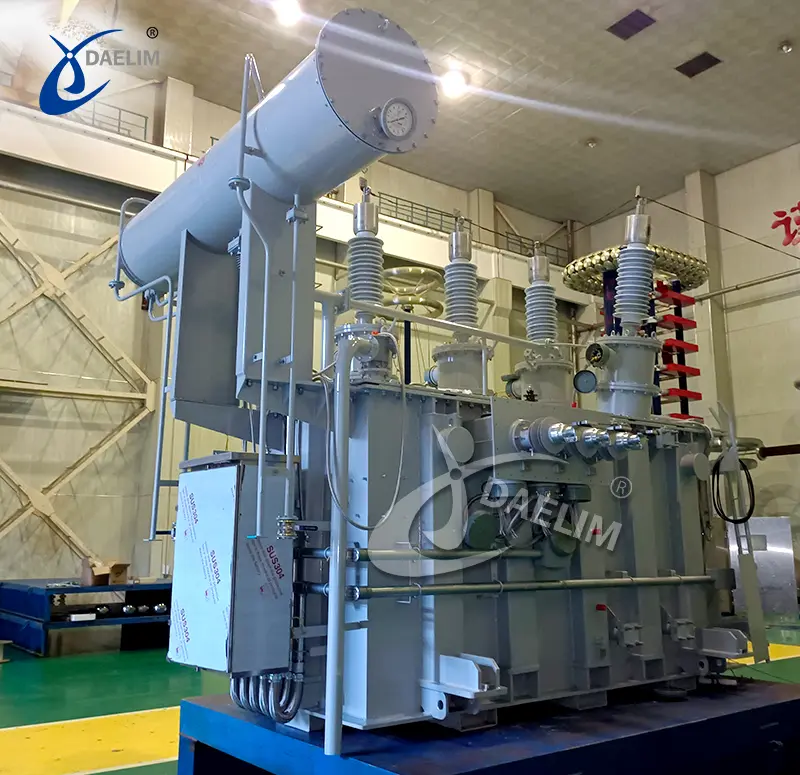
A corrugated conservator looks like an accordion. While it does contain folds or ridges, it is those ridges that expand and contract with the oil as its temperature varies. Here is how it works:
- The ridges may expand and contract with the changes in oil level.
- This design is helpful in that it changes automatically depending on the oil level without the use of many extra parts.
- The corrugated structure also seals off the oil from outside air. In this way, dust as well as moisture cannot enter inside.
This type of conservator is simple and practical; that is why it is most used in transformers.
Capsule Conservator
The capsule conservator differs from the two previously discussed conservators. The capsule or bag inside which the small volume of oil is conserved is sealed hermetically, and hence, the oil is saved from air and other external factors.
Here’s how it works well:
- The oil is stored in the capsule, which subsequently expands and contracts with the oil's temperature.
- Since it is sealed within a capsule, there is no contact with outer air, dust, or moisture.
- This will keep the oil very clean, which is beneficial to the overall health of the transformer.
The capsule conservator is often used in places where keeping the oil extra clean is very important.
Diaphragm Conservator
The diaphragm conservator nearly functions like a capsule conservator but differs in having a flexible diaphragm or rubber sheet instead of a bag. This sheet separates the oil from the air within the conservator.
Here's how it helps:
- The oil level would make the diaphragm move up and down, separating oil and air.
- It separates the air coming into contact with the oil, making it clean.
- This also helps control temperature without letting moisture or dust into the system.
This type is good for transformers in exposed locations because the outer conditions need to protect it further.
Advantages of Conservator Transformers
Conservator transformers offer power systems with several benefits to improve their reliability and efficiency. The most important advantages of the conservator transformer are:
Improved Oil Quality
The conservator keeps the oil pure by not letting dust move towards it. This protects the oil from direct outdoor air and reduces moisture and dust etc. from going inside the oil.
Enhanced Temperature Control
The conservator system allows the oil to expand and contract with the change in temperature. When heated, oil expands and occupies the conservator tank, and when it is cooled, it returns to the main tank.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
Conservator transformers require little maintenance because they can keep the oil clean and the temperature controlled. Since they're designed to limit the exposure of air and contaminants, frequent oil testing, filtering, or replacement is not required.
Improved Operational Safety.
Conservator transformers prevent overheating and insulation breakdown, which leads to hazardous situations. This adds an extra level of protection to both the transformer and operators.
Conclusion
Choosing the right transformer is one of the important factors to power systems reliability, efficiency, and safety. Oil capacity, cooling, and protection against contamination are some of the important considerations that would ensure better performance with reduced maintenance.
Daelim's conservator transformers are designed with strength, supporting voltages up to 345 kV and power ratings up to 500 MVA. They are designed and manufactured based on the ANSI/IEEE, CSA, IEC, AS/NZS, GOST, and NEMA standards. With extensive experience in conservator transformer projects across North America, Europe, Australia, and other regions, we have a proven track record of delivering high-quality solutions.
Ready to find the perfect fit? Contact us for expert guidance and tailored solutions!



