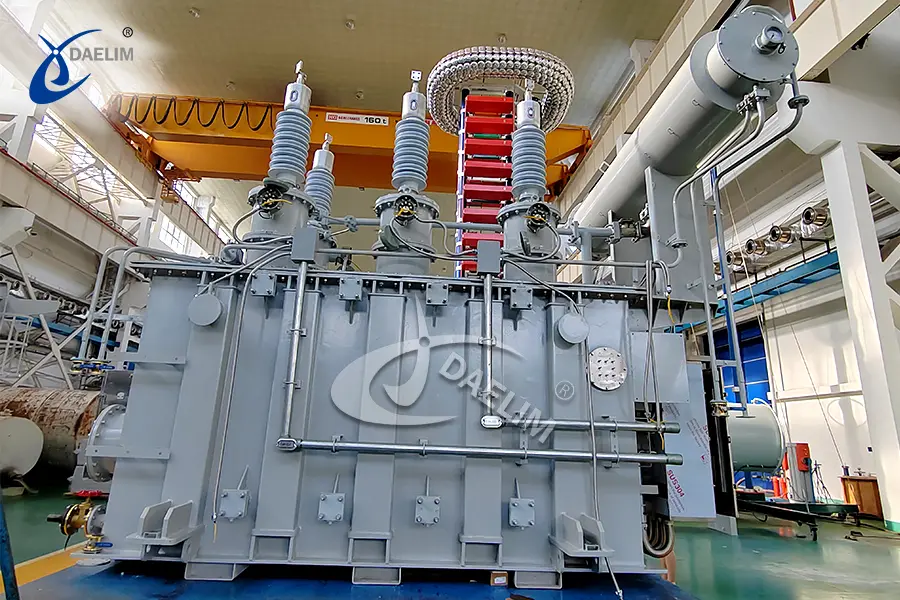
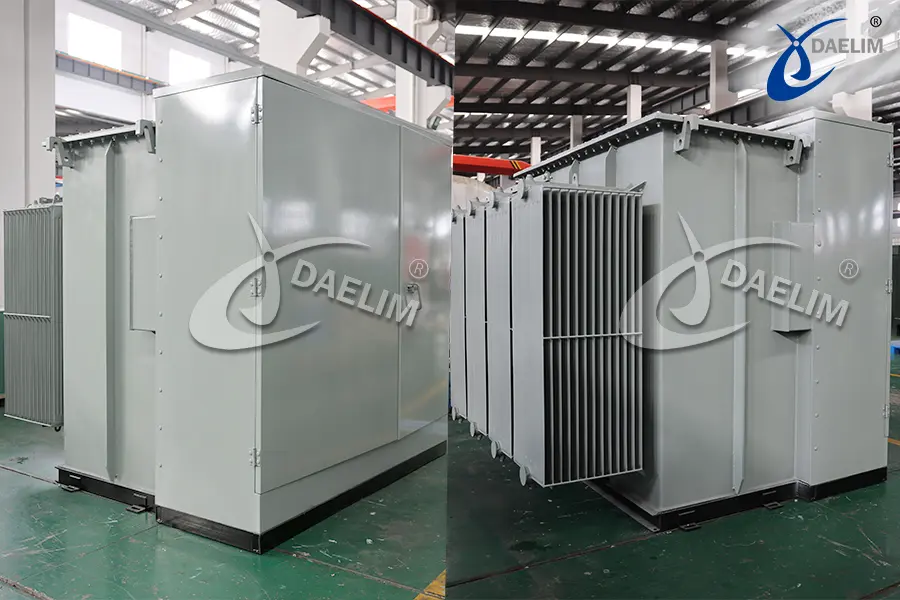
Basic Guide Of Electrical Transformer

Electricity is an essential part of our daily lives. It powers everything from small electrical devices in our homes to huge electrical setups in commercial industries and manufacturing sites.
However, the electrical supply available is not always compatible with your application. For example, the bulk of power loads from the electrical grid would fry your phone if you use it directly for charging.
So, how is this electricity supply made safe for use? That is where the electrical transformer came in.
In a nutshell, a transformer literally transforms energy or electricity to different voltages at a certain level to make it more suitable and safe for actual use.
In this article, we’re going to take a closer look at electrical transformers and answer some frequently asked questions like what does a transformer do, how does a transformer work, and explore some of the common electrical transformer types.

Daelim is a professional transformer manufacturer which has been in the business for over two decades and has been a committed partner in producing world-class transformers all over the region covering some of the largest markets like America, Australia, and Europe.
Up to now, Daelim never stops to discover new ways to innovate and find strategies to keep up with the ever-changing demands of the market. With its unparalleled commitment to deliver high-quality transformers, safe electricity is always close at hand.
Contact Daelim TransformerWhat Is a Transformer?
A transformer is a static electrical device used to convey power across a circuit or several others in various electricity lines and other power sources, typically for safe transmission and to step up or down the voltage rate, depending on a specific requirement.
The simplest form of transformer and probably the most popular one is the pole-mounted transformer. These are those small-sized barrels attached to utility poles. Moreover, larger transformers are also available.
Other large-capacity transformers can emit significant amounts of heat. Heat is generated as a way to release excess transformer energy and for the entire system to cool down, with that, they are required to be confined to an area with less traffic for safety.
Apart from the size and capacity, transformers can be further categorized according to their function, core material, output, cooling system, and many others.
Electricity and why do we need to transform it?
Electricity is power but where does power come from? Power can come from various sources like fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewable energy sources.
These sources in their raw form are called potential energy and only become useful when transformed into another form of energy like electricity.
Electricity is produced by using several energy conversion technologies. Coal is the main source of power across the world. So, how is coal converted into electricity?
Power plants burn coal to produce heat energy. This energy goes to the boiler to produce steam to run the turbine.
Once the turbine is activated, the energy produced is used to power the generator that ultimately generates the end product which is electricity.
Now let’s figure out why we need to transform electricity.
Primarily, transforming electricity has a lot to do with delivery, efficiency, and safety. The bulk of electricity needs to be transformed multiple times before it reaches the service area which is our homes, offices, and industries.
The most efficient way to do the job is to use transformers. But, what does a transformer do with electricity?
Let’s take a look at a simple example here and then later on we will dig deeper into how does a transformer work.
Electricity is made available from the source, for example, from a power station. At this point, electricity has to be transformed at a higher voltage to reduce current, avoid losses, and conserve energy.
To make this possible you will need a Step Up Transformer to effectively increase voltage before and while it is being transported in cables over long distances in the transmission lines.
The next stop would be the substation. Remember, it is transmitted at a high voltage and for it to be ready for consumption voltage must be reduced first.
Depending on the distance, electricity will have to pass through two or more Step Down Transformers to decrease the voltage to a more manageable level most suitable for the service area, normally at 120 to 240 Volts.
At this rate, you can now enjoy and access an unlimited flow of electricity which is workable and safe for your electrical devices.
How do transformers work?
A transformer is a device that regulates or alters voltage and makes it flow in an electrical system that works according to Faraday’s Law also known as Electromagnetic Induction.
What is Electromagnetic Induction?
Electromagnetic induction allows electron transfer without the actual connection. Induction happens when the electromagnetic force is produced. This force is from varying electromagnetic fields which in turn facilitates the transfer of electrons between conductors.
Here are some of the requirements of the basic transformer setup:
- Alternating current generator - this is your power source
- Conductors - this serves as the primary and secondary coil connecting the source and the load
- Electrical load - this is what you intend to power. For example, a light bulb.
Why alternating current and not direct current?
When an alternating current is supplied to the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field with fluctuating strength and orientation.
This change creates a magnetic flux, it sends varying signals and excites the electrons on the other side. It then forces them to move to the nearby conductor which is the secondary coil.
In the case of direct current, a magnetic field is still produced but most likely steady. Thus, induction or electron transfer is impossible.
How does a transformer coil work?
Coils are also known as windings. A transformer is composed of two windings called the primary and secondary windings.
The primary windings serve as the connection from the source and the secondary winding serves as the inducted side which becomes the outlet of the final voltage produced.
Some transformers have multiple windings which can have two or more windings on the primary or the secondary side.
At a glance, the coils serve as a passageway of electricity but more than that, know that how does a transformer work is greatly affected by its coil arrangement.
So, How is the desired voltage output of a transformer manipulated?
The answer lies in the coil configuration of both the primary and secondary sides. The transformer electrical power is determined by the number of turns on each coil or windings.
To step up or increase the voltage output, there should be more turns on the secondary side compared to the primary side.
Conversely, to step down or decrease the voltage, then the primary side has to have more turns than the secondary side.
Parts of a Transformer
Coil/Windings
 Primarily serve as a pathway for electricity with the aid of magnetism. The number of turns in between windings and its ratio sets the final voltage.
Primarily serve as a pathway for electricity with the aid of magnetism. The number of turns in between windings and its ratio sets the final voltage.
Each strand is made with highly conductive materials such as aluminum and copper. These materials also minimize the resistance and help increase the overall efficiency of the transformer.
Apart from using good material, adequate insulation should be added to prevent losses and avoid breakdowns.
Iron Core
This part can strengthen the electric transformers’ magnetic field a hundredfold depending on the material used. Some of the materials commonly utilized are iron, laminated silicon steel, and special alloys.
The design can either be a shell type or a core type. The Shell Type uses an E-I or E-E lamination pattern to form the core while the Core Type uses L or U-I lamination pattern.
Insulation
This serves as a barrier and protection between the windings and the core. It also plays an important role in the cooling system, support, and the lifespan of a transformer
It is mostly made of liquid material like transformer oil, gas material such as fluoro gas, and solid materials like electrical grade paper, pressboard, wood, and insulating tape.
In choosing the right insulation material, the resistance, permittivity, and dielectric strength should be considered.
Different Types of Transformer Windings
Configuration of the windings varies depending on the electrical transformers types and rating.
Cylindrical Winding
The insulated coils are winded down following a cylindrical pattern typically done with multiple layers for added strength and to avoid the turns from dislodging.
This arrangement provides maximum exposure to the coolant and thus, improves the efficiency of the cooling system.
However, the structure of the design is less sturdy which is why it is more suitable for small-scale transformers. A multi-layered cylindrical winding can operate up to 800 kVA.
Helical Winding
A multi-layered winding wherein two or more coils are arranged toward a single direction to make a turn forming a helical pattern.
Its configuration provides an adequate stacking factor that is useful in forming a solid structure that supports the overall stability of the windings.
This is applicable for core-type transformers whose output is not more than 1000kVA.
Sandwich Winding
In this type, the windings are divided into two or more sections arranged in a way that high-voltage winding is sandwiched in between to low voltage windings.
To reduce impedance and enhance the cooling process, more sections should be added. Moreover, it would be more tedious and would make it more difficult to insulate the windings.
This type of winding is often used in shell-type transformers.
Types of Liquid-Filled Transformers
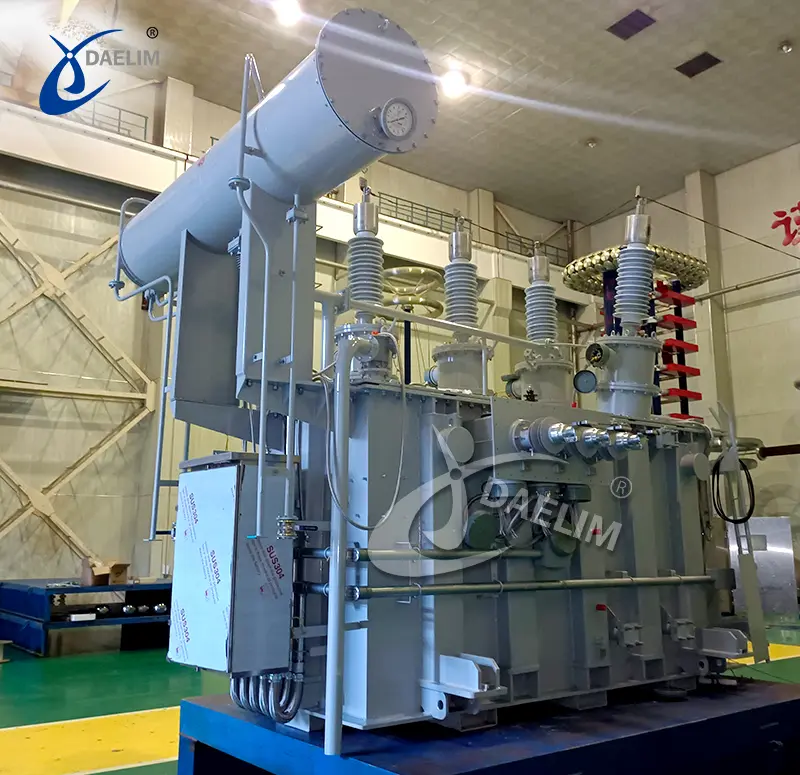
HV power transformers
A tried and tested core component to efficiently transmit and deliver power. It helps regulate power and avoid energy loss while electricity traverses the transmission lines.
HV power transformers are among Daelim's expertise. They are manufactured and tested in compliance with ANSI/IEEE C57.12.00, CSA C88, AS/IEC 60076 and EN Std.
Daelim currently caters HV power transformers to various countries, such as America, Canada, Mexico, Australia, Ecuador, etc.
Basic Guide To High Voltage Power Transformers
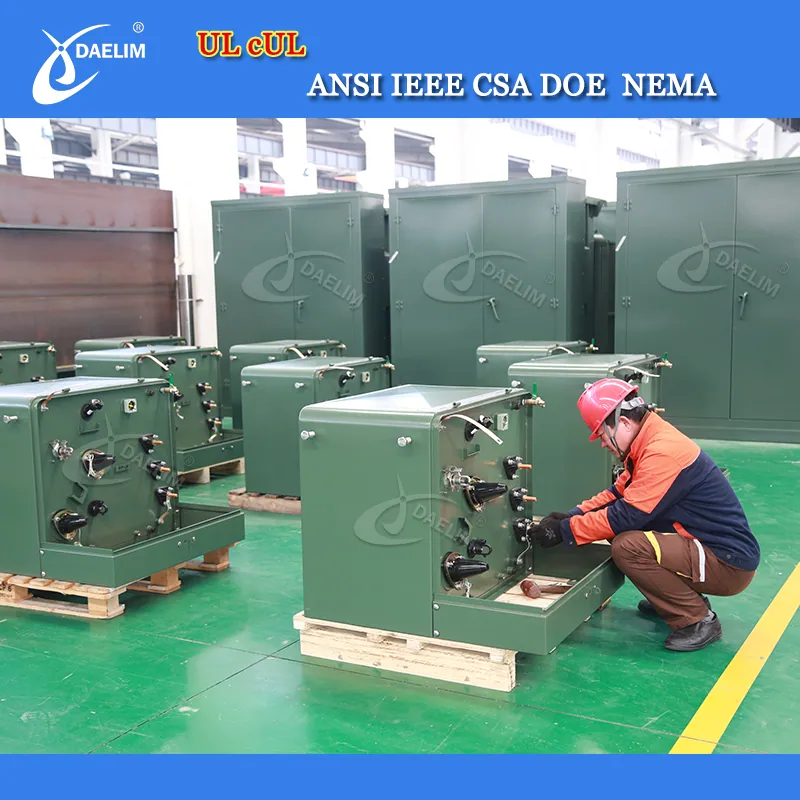
Padmount transformers
 It is one of the safest types of distribution transformers. It doesn’t need additional enclosure as the unit is secured in a metal cabinet on top of a concrete pad.
It is one of the safest types of distribution transformers. It doesn’t need additional enclosure as the unit is secured in a metal cabinet on top of a concrete pad.
They’re mainly used as a step-down transformer for underground power distribution in commercial and residential areas. Pad mounted transformers also have single phase and three phase two types, compared to the pole mounted transformers, pad mounted transformers are easy to install and repair. They are the most common transformer in our life, you can see them in your front yard, they are for the power supply of your house. Pad mounted transformers are also wildly used in data centers, bitcoin mining farms, solar power farms, etc... Pad mounted transformers are also called electrical transformer boxes, or “the ugly green box in my yard”.
3 Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
Daelim has a wide array of Pad-mounted transformers carefully manufactured in adherence to prevailing IEEE C57.12.4, CSA C227.4, and other international standards like ANSI, DOE, CSA, and NEMA.
Pad-mounted transformers from Daelim are also highly customizable using high-quality brands like Qualitrol, ABB, and Eaton.
Substation Transformers
 They serve as an intermediary transformer used to transmit and distribute power, subsequently to step up or down the voltage according to its application.
They serve as an intermediary transformer used to transmit and distribute power, subsequently to step up or down the voltage according to its application.
It normally functions remotely without actual intervention. Units are often installed under harsh conditions and so, choosing the right manufacturer is critical.
Daelim substation transformers are one of the safest options you can have. Units are carefully designed to thrive even in the most challenging environment.
Part of the process is strenuous testing to ensure quality, safety, and conformance to IEC and IEEE standards.
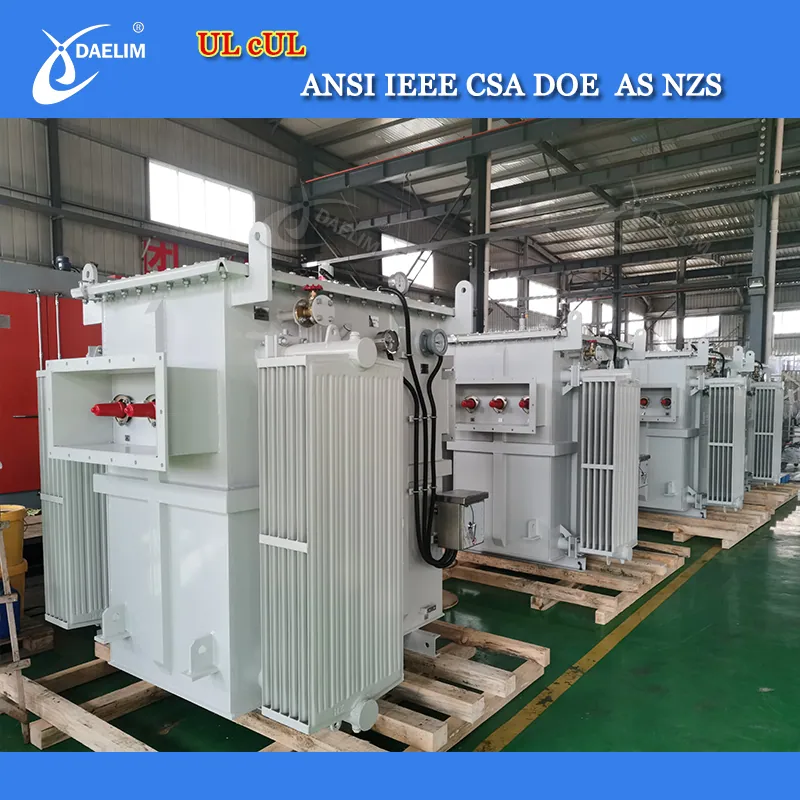
Pole Mount Transformers
 A classic workhorse in the energy sector. It serves as the end receiver of electricity that transforms power to a disposable level.
A classic workhorse in the energy sector. It serves as the end receiver of electricity that transforms power to a disposable level.
This type of electric transformer is a staple in every distribution system prevailing in rural areas typically installed on utility poles.
Pole-mounted transformers by Daelim are among the fast-moving products across North America.
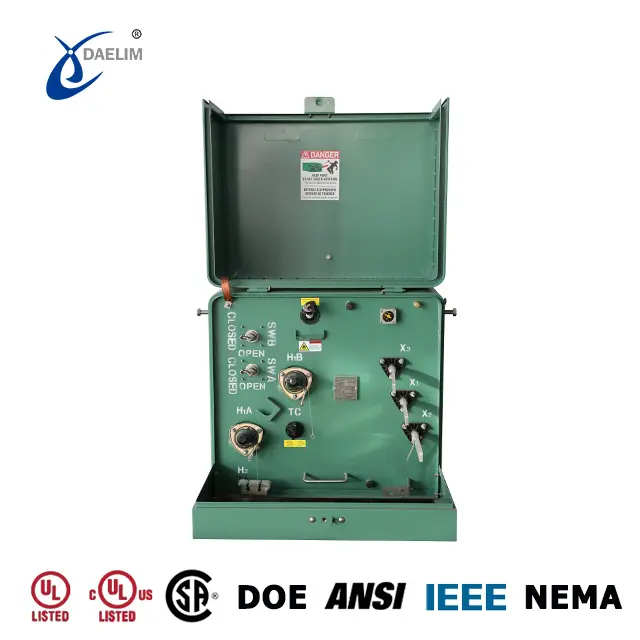
Taking pride in offering not just the conventional type but the top of the line Completely Self Protected(CSP) type.
The CSP type provides multi-level protection including a built-in protective fuse, integrated high-voltage side surge arrester, and low-voltage side circuit breaker.
CSP VS Conventional Transformer : Which Is Better?
To maintain the credibility of the product, Daelim duly secures necessary certifications from UL, CSA, CESI, and together with other trusted third-party certification bodies like SGS.
Autotransformers
A subtype of HV distribution transformer. One of its prominent features is its single winding. Compared to its counterpart, autotransformers are known to be more economical and efficient in terms of voltage regulation.
Daelim autotransformers are designed with respect to the IEC standards. Other than Autotransformers, Daelim offers a wide collection of distribution transformers.
Electric Furnace Transformer
 This type is designed to energize electric furnaces particularly used in smelting various ore to extract high-valued metals like steel, copper, and silver.
This type is designed to energize electric furnaces particularly used in smelting various ore to extract high-valued metals like steel, copper, and silver.
It is further classified into three types:
Resistance Furnace Transformer
Shell Furnace Transformer
Electric Arc Furnace Transformer
Electric furnace transformers from Daelim are among the specialty transformers that are engineered and tailored according to the client's needs.
Read more: How Much You Know For The Different Types Of Transformers?
What Does An Electrical Transformer Look Like?
Different types of transformers also look different. Our common single-phase pole mounted transformers are round-through types. The single-phase pad mounted transformer is square like a box, and its lid is top-opening. Pole mounted three-phase transformers are also commonly seen. The high and low voltage bushings are ejected, and the oil tank is rectangular. The shape of the three-phase padmount transformer is similar to his name, and the front view looks like a metal box. These are relatively regular in shape. There are also some medium and large transformers. Due to their large capacity, they need more protection devices, heat sinks, etc. The appearance is not very regular, but they are very large and heavy.
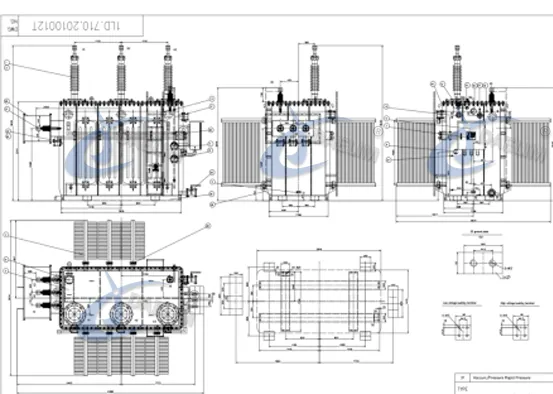
Electrical Transformer Drawing
The electrical transformer drawings below are designed by Daelim.
HV Power Transformer Outline Drawing

Pad mounted transformer drawing

Single phase pad mounted transformer

How Are Different Types Of Transformers Depicted In Diagrams?
Diagrams can be highly used to show the construction of electrical transformer types.
Power Transformer Diagram
A power transformer has a diagram that is consisting of a rectangular or square box with two sets of wires. The main one and the second one, are each represented by an independent coil. A solid line within the box is commonly utilized to represent the core, which generates an electric path.
Distribution Transformer Diagram
Typically, the distribution system diagram shows both the primary and the secondary circulation circuits together with their matching connections to the core. The wires appear as an arrangement of connected coils or loops.
Temperature control and transmission voltage level modification are made available by these types of transformers with diagrams.
Autotransformers Diagram
These types of transformer with diagram typically appears as a single coil in an illustration, frequently with a pressing point along the length of the winding. The schematic shows the input and output links, which are frequently denoted by terminals or wires.
The magnet's route is generally established by the core, which is apparent inside the coil. Above all, it's essential to keep in mind that transformer construction may be more complex than what is generally shown in simplified diagrams. These types of transformers with diagrams serve as visual aids to comprehend the components and connections of transformers types.
Learn more about Transformer Diagram
What Should I Know Before Purchasing A Electrical Transformer?
Depending on different projects, there are different levels of a transformer purchase:
Direct purchase
For direct purchase, please share the basic information of your project below:
- Rated Capacity (kVA/MVA):
- Input Voltage (V/kV): also called high voltage, primary voltage.
- Output Voltage (V): also called low voltage, secondary voltage.
- Purchase quantity (units).
- Which country will the transformers be installed in?
With this basic information, the Daelim team can prepare a suitable offer for you as soon as we received your inquiry.
Also if you have requirements regarding the lead time, please also share them with us. So Daelim's production team can calculate our production schedule and offer you a perfect production time.
Get it now: How to purchase a 2 MVA power transformer?
Public tender project
If it is a public tender project, there will be tender documents including the technical requirements of the manufacturer, production and testing standard, accessories, and the transformer itself.
Daelim Belefic has supported our clients to win a lot of contracts in the North American market, Latin American market, Australian market, Southeast Asia market, Middle Asia market, etc...
Daelim engineer team will make the most suitable solution based on the project requirements, and we will support our customers with the most competitive price, 24/7 online technical support, 2-year warranty, and after-sales service if it’s necessary.
What Are The Key Considerations When Selecting Electrical Transformer Types For A Specific Application?

Finding the necessary voltage level transformation must come first. To match the voltage needs of the application and assure compatibility with the power supply and load, it is necessary to determine which power transformer types are necessary.
It is also important to take into account the kind and specifications of the load that the transformer is supporting. The types of electrical power transformers to use depends on the characteristics of the load, such as its resistive, inductive, or capacitive behavior.
During the selection process, factors like power, harmonics, and the transient behavior of the load should be carefully examined. It is essential to adhere to all applicable safety rules, industry standards, and municipal electrical codes for each electrical transformers types.
Its quality, safety, and compatibility with the electrical system are highly guaranteed if the chosen types of electrical power transformers comply with necessary standards like IEC, ANSI, and NEMA.
Finally, expenses are important. The overall price-effectiveness of the power transformer types can be highly established by analyzing both the initial cost and the long-term operational and maintenance expenditures.
In relation to the particular application, elements including the cost of purchase, reliability of energy, reliability, and anticipated lifespan should also be highly considered.
Electrical Transformer Connections
 In order to create power connections between the two main wirings, electrical transformer connections must be first established.
In order to create power connections between the two main wirings, electrical transformer connections must be first established.
There are some electrical transformer connections arrangements:
- Delta Connection
- Star Connection
- Zigzag Connection
- Wye-Delta Connection
- Scott Connection
As well as that, the particular application, energy ranges, phase needs, and load parameters all affect the electrical transformer connection choices. Each connection construction offers a unique set of benefits and adaptability for various electrical installation types.
To ensure adequate voltage conversion, phase connections, and successful power transfer between an electrical transformer type, precise design, and configuration of the transformer connections are necessary. Therefore, when you choose an electrical transformer supplier, you must choose a very professional and experienced one.
The Ultimate FAQs Guide To Transformer Connection
How To Choose Electrical Transformer Manufacturer?

Check the manufacturer's international project experience: Ensure that the manufacturer has experience in the international electrical transformer business and is familiar with the standards of your country. This is essential as different countries have different standards for transformers.
Review technical specifications and drawings: Before placing an order, request technical specifications and reference drawings from the manufacturer. These documents should align with your project requirements and local standards. Verify with your engineering team to ensure compatibility.
Verify transformer certifications: Check if the manufacturer holds relevant certifications such as CSA (Canadian Standards Association). Lack of certifications may indicate limited international experience.
Transformer testing reports: Request testing reports for similar transformers to ensure quality and reliability. Confirm with your engineer that the testing procedures and results meet industry standards.
Consider third-party inspection: If you have doubts, consider sending a third-party inspector to the manufacturer's facility before making a purchase. This ensures an objective evaluation of the factory's capabilities and production processes.
Read my article on How To Choose The Suitable 110KV Power Transformer?
Electrical Transformer Shipping


For large electrical transformers, it's best to ship them by sea because they're too large and heavy for air travel. Sea freight is common and works well for heavy loads. But you need a reliable shipping agent who knows how to handle oil-filled transformers.
Sometimes, small electrical transformers can be sent by air if it's urgent. But first, the oil inside needs testing for safety. If it passes, the oil is removed and replaced with nitrogen gas for the flight.
Proper packaging and shipping are super important to prevent damage from rust or corrosion during long sea trips. Choosing an experienced manufacturer should make sure your transformer arrives safely.
What Can Daelim Transformer can help you?
Professional Engineering Support
Daelim has skilled engineers who know US, Canadian, and international standards, providing custom solutions for projects.
Technical Plans and Drawings:
With over 20 years of experience, Daelim offers technical solutions and drawings meeting different transformer standards.
Certifications
Daelim holds certifications like CSA, UL, cUL, and CE for transformers, ensuring quality and compliance.
Testing Reports
They provide test reports from reputable organizations like SGS and CESI, plus IEC type test reports.
Welcome Visits
Customers can visit Daelim's offices and factories, meet the team, and see production facilities and testing.
In-Stock Availability
Located in Houston, USA, Daelim's warehouse has many transformers in stock for immediate shipping. If not in stock, new transformers take 8-12 weeks for delivery.
Transportation Solutions
Daelim partners with experienced shippers for safe and fast delivery. They offer customized shipping and can arrange air freight if needed.
Maintenance Requirements For Different Electrical Transformers
 The maintenance requirements for every electrical transformer type can vary based on their type, size, and the environment in which they are generally used. However, there are common practices that apply to most, if not all, power transformers types. These include:
The maintenance requirements for every electrical transformer type can vary based on their type, size, and the environment in which they are generally used. However, there are common practices that apply to most, if not all, power transformers types. These include:
Visual Inspection: Regular visual checks should be thoroughly performed to identify any apparent signs of damage or wear, such as leaks, rust, or signs of overheating.
Oil Testing and Replacement: For certain types of electrical power transformers, the oil should be regularly tested to ensure it is free from moisture and other contaminants. The oil may need to be frequently replaced periodically or treated to maintain its insulating properties.
Electrical Testing: Various electrical tests, such as turn ratio tests should be periodically performed to check the transformer's electrical performance.
It's important to note that the maintenance of certain power transformer types should be highly performed by trained professionals following the manufacturer's guidelines and relevant safety procedures.
Overall, maintenance for types of electrical power transformers is critical to ensure reliable operation, extend the service life of the transformer, and prevent costly and potentially dangerous failures.
Electrical transformers are everywhere. Right in our homes, offices, and industries, wherever there's a need for safe electricity, electrical transformers are present and are here to stay.
Whatever your transformer requirements are, whether it’s a simple pole-mounted transformer or a large-scale specialty transformer, Daelim always has something to offer.
Do you still have questions regarding transformers? Or do you need to speak with an expert? Contact Daelim Transformer now!
Related Products
Related Article
Three Phase Power Transformers for Bitcoin Mining Facility in Texas!
Daelim Transformer thrilled to share details of our project - the supply of 90 units of three-phase power transformers for a large-scale Bitcoin mining operation in Odessa, Texas. Each transformer is rated at 2500(3000)KVA with a primary voltage of 34.5kV Delta and a secondary voltage of 480GrdY/277. With strict UL certification requirements and a focus on high-quality accessories from reputable brands, this project demanded precision, efficiency, and reliability.
20MVA Power Transformer for the United States
This project involves the development of a 20 MVA three-phase power transformer tailored for the United States market. The primary voltage is 24.94kV, and the secondary voltage is 4.16kV, indicating it functions as a step-down transformer. The design and production fully comply with IEEE C57.12.00 standards and have passed third-party UL team testing. All accessories also adhere to IEEE standards. FR3 vegetable oil serves as the insulating liquid for the transformers.
2 MVA Pad Mounted Transformer for Utility
Behold the backbone of Canada's utility infrastructure—the 2MVA pad mounted transformer. With a primary voltage of 4160Grdy/2400V and a secondary voltage of 800GrdY/461V, this transformer stands as a testament to efficiency and reliability in power distribution. Crafted in strict accordance with CSA standards and CAN/CSA802.1 energy efficiency guidelines, it embodies the pinnacle of engineering excellence.
Canadian 69 kV Substation Transformer Project
Today, we are excited to present a case study on a 69 kV substation transformer project by Daelim Transformer. Our Canadian client required a step-down transformer for their substation to connect with the hydroelectric grid in Quebec.
Pad Mounted Transformer for BESS System 4.0 MVA in Riverside County, California
Today, Daelim Transformer is proud to introduce a pad-mounted transformer for a 4.0 MVA Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) project located in Riverside County, California. The transformer is meticulously crafted to comply with the specifications outlined in the California Electrical Code Article 450.
4500 kVA Substation Transformers for Australian Mining Site
Today, we introduce a project by Daelim Transformer aimed at supplying transformers to a mining site in Australia. This project entails the provision of two units of 4500 kVA substation transformers tailored to fit the narrow confines of mining tunnels. Due to space constraints, the transformers need to be compact in size and mounted on mobile racks for easy maneuverability within the mine shafts. This necessitates meticulous design to meet the strict dimensional requirements set by the client.















