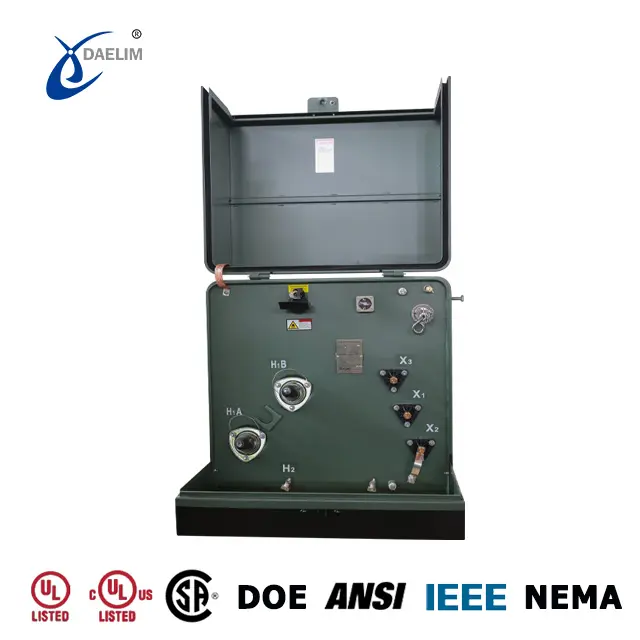
Guide to Tap Changer in Pad Mounted Transformer
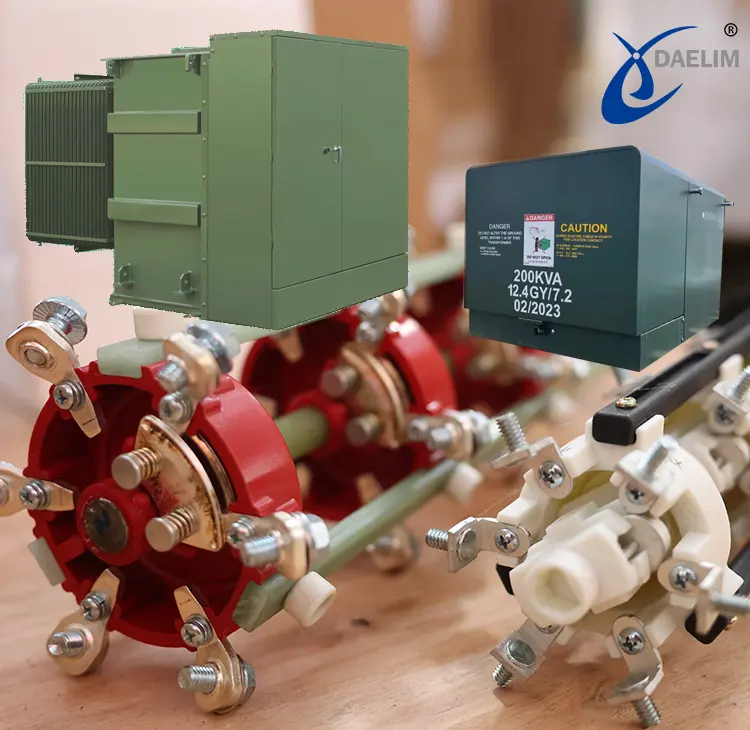
Pad mounted transformer play a pivotal role in facilitating efficient energy distribution and management in various applications. Among their key components, the transformer voltage regulating switch, commonly known as the tap changer, stands out as a crucial accessory. In this article, we delve into the significance of tap changers in pad-mounted transformers, their types, functions, and the importance of voltage regulation in ensuring optimal performance and reliability

Daelim Transformer undertakes hundreds of pad mounted transformer projects annually and exports thousands of pad mount transformers to the Americas each year. We possess extensive expertise in the standards, design, requirements, and accessories of pad mounted transformers. Consequently, we are well-equipped to fulfill the tap changer requirements of any pad-mounted transformer project you may have. Additionally, our pad mounted transformer with a full range of UL listed.
At Daelim Transformer, we maintain a diverse inventory of pad mounted transformers with taps in various sizes and configurations. Whether you require a transformer with specific voltage regulation taps or seek further information on this topic, please do not hesitate to Contact Us.
Contact Daelim TransformerWhat is the transformer tap changer?
The transformer tap changer is a vital device for regulating voltage within a transformer unit. This device effectively adjusts the output voltage by manipulating the turns ratio of the primary and secondary windings. Achieving this regulation necessitates the incorporation of multiple taps in the high-voltage winding of the transformer, enabling seamless switching between them. The voltage regulating switch(also called tap changer) alters the voltage ratio of the transformer by adjusting the number of effective turns, thereby achieving the desired voltage regulation effect.
What type of tap changer is used for pad mounted transformer?
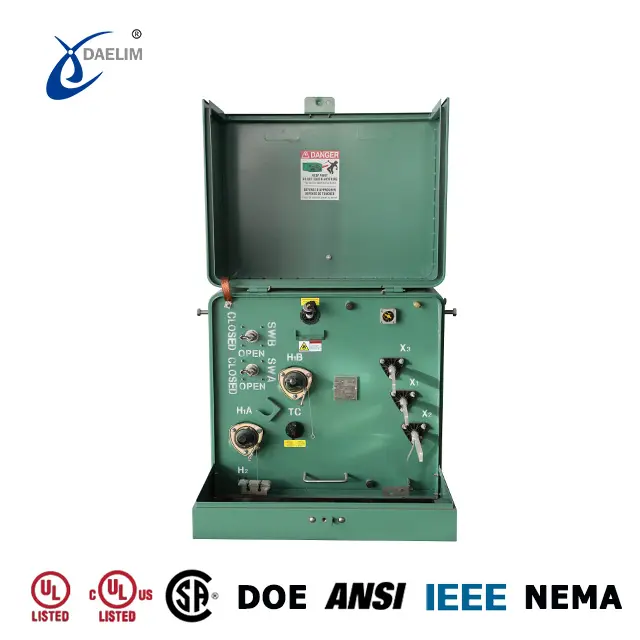
Pad-mounted transformers typically utilize non-excitation cage-type external tap changers, which can offer five, seven, or sometimes three switch positions. They are available for both single-phase and three-phase pad transformers and are usually installed on the side wall of the fuel tank. The cage switch is easy to install, operate, and safe. It doesn't require any special tools, as it installs through a keyhole in the tank wall and is sealed with an internal gasket.
External switches eliminate many of the hazards associated with manual internal switches, as line workers do not need to come into contact with high-voltage conductors and transformer liquid. Only a hot rod is needed to adjust the transformer gear. The transformer tap changer can adjust the voltage without requiring the transformer to be disassembled, thus avoiding contamination inside the transformer tank.
3 Position Tap Changer
The pad mounted transformer sometimes uses a 3-position tap changer, featuring one tap at 5% increments above and one below the nominal nameplate voltage rating. The three-position tap changer can have a voltage regulating range of ±5%, which is uncommonly used in pad-mounted transformers.

5 Position tap changer
- The 5-position tap changer is the most commonly used among pad-mounted transformers. In this setup, the high-voltage winding of the transformer will have 5 tap leads connected to the tap changer, providing a voltage regulation range of ±2*2.5% of the rated voltage.
- Typically, there are two gears above the rated voltage and two gears below. This is the standard configuration for pad-mounted transformers. However, in some transformers, the remaining four gears may be lower than the rated voltage, with each gear's voltage being 2.5% lower than the previous gear.
- The tap changer configuration mentioned above is not fixed. The rated voltage level can be set at the second position, allowing for adjustment up by one level and down by three levels. Many of the Blockchain projects we undertake involve pad mounted transformers. To accommodate multiple public voltage connections, the adjustments between the tap changer gears are not uniform. For example, 14.4kV, 13.8kV (rated voltage), 13.2kV, 12.47kV, 12kV. The specific configuration can be determined according to the actual application requirements.
7 Position Tap Changer
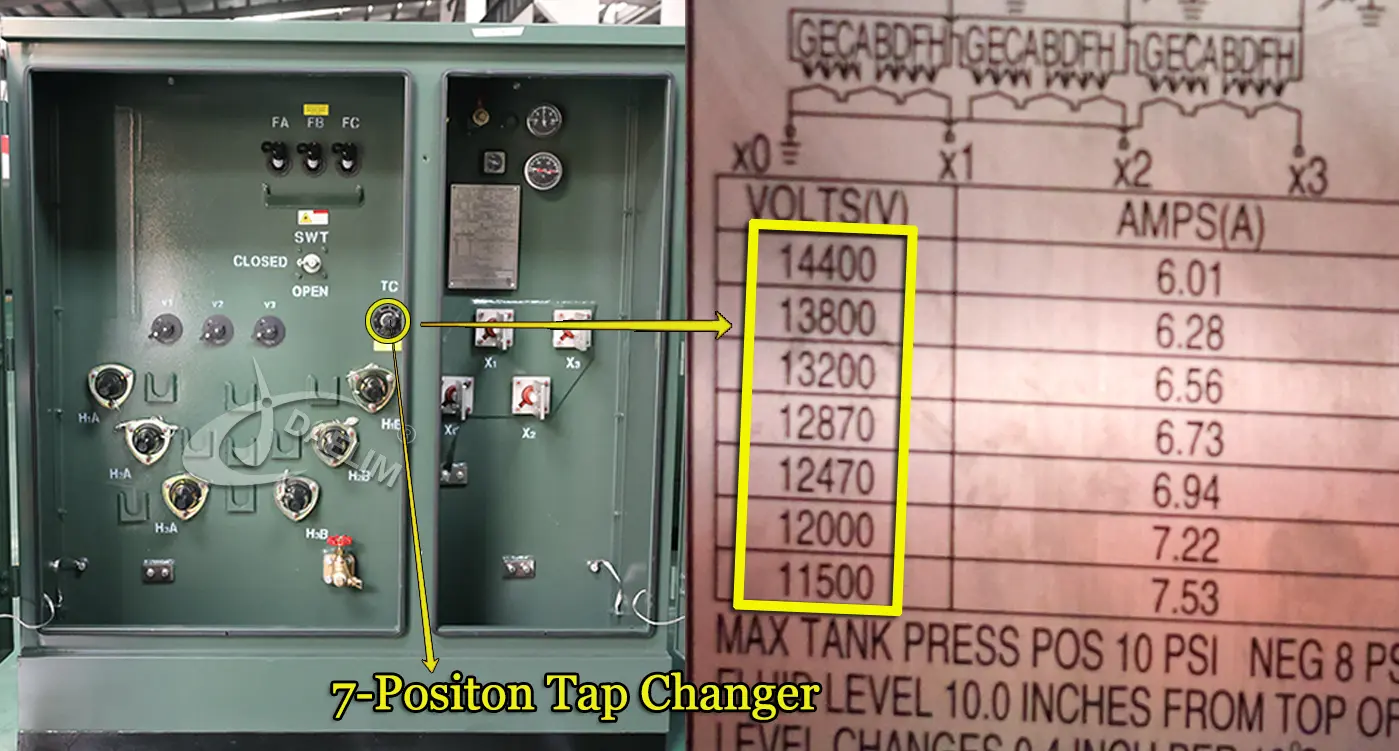
When Daelim Transformer was involved in pad-mounted transformer projects in the Americas, some customers also requested a 7-position tap changer. These tap changers allow for adjustments to the high-voltage winding with 7 tap leads, enabling three gears above and three gears below the rated voltage. The voltage increment and decrement of each gear can vary, and the configuration of this switch is not fixed. The rated gear can be positioned according to specific requirements.
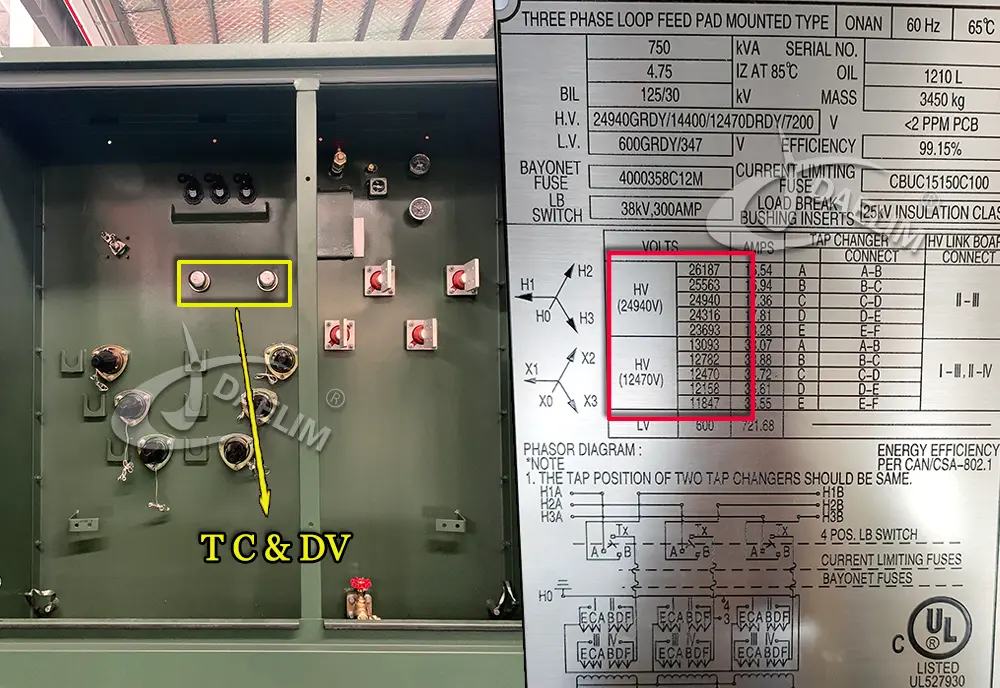
In addition to designing pad-mounted transformers with 3 positions, 5 positions, and 7 positions tap changer, Daelim Transformer can also design dual high-voltage or dual low-voltage pad mounted transformers with a dual voltage switch. Contact Daelim Transformer now to receive a quotation for a pad mounted transformer immediately.
What happens if the pad mounted transformer with a higher or lower voltage?
The ideal operating voltage for the pad mounted transformer is at its rated voltage. However, due to system voltage fluctuations caused by load changes during operation, the actual voltage applied to the transformer often deviates from the rated voltage. Having a voltage higher or lower than the rated voltage can result in adverse effects.
Adverse effects of higher voltage of the pad mounted transformer
The harm caused by a transformer power supply voltage higher than the rated voltage is mainly manifested in two aspects.
- Firstly, when the transformer operates at its rated voltage, the magnetic flux density in the core approaches saturation. If the power supply voltage exceeds the rated voltage, the excitation current will increase sharply, leading to a decrease in power factor and a rapid rise in transformer temperature, potentially causing winding burnout. When the voltage exceeds 105% of the rated voltage, more high-order harmonics are generated in the transformer winding, increasing the risk of insulation damage.
- Secondly, if the primary side voltage exceeds the rated voltage, the secondary side voltage of the transformer will also increase accordingly, potentially causing overload, insulation breakdown, or even burnout of electrical equipment. Therefore, the primary voltage must not exceed 105% of the rated voltage.
- Regarding hazards to electrical equipment, excessively high transformer voltage will lead to increased output voltage. This can overload electrical equipment, shorten its lifespan, or even cause fires. Additionally, high voltage can increase equipment current and temperature, leading to insulation loss under high-temperature conditions.
Adverse effects of lower voltage of the pad mounted transformer
- Reduced transmission capacity of the transformer, limiting the full utilization of electrical equipment.
- Increased current due to low power supply and output voltage, leading to higher losses in the line and transformer, resulting in elevated network loss. For example, if the line voltage decreases by 15%, line loss will increase by 32% accordingly.
- Decreased output power of motors when the voltage drops below 80% of the rated voltage. This reduction can reach about 36%, while the current increases by 20% to 30%, and the temperature rises by 12% to 15%.
- Diminished brightness of incandescent lamps by approximately 30% and fluorescent lamps by about 10% when the voltage falls below 90% of the rated voltage. If the voltage drops below 80% of the rated voltage, fluorescent lights may fail to light up, and TVs may exhibit distortion, impacting people's daily lives.
Try for free: Pad Mounted Transformer Accessories
How does a transformer tap changer work?
A tap changer typically comprises multiple taps, each connected to a different winding of the transformer. By selecting different taps, the effective number of turns of the winding can be altered, thus changing the output voltage of the transformer.
The tap changer's operating mechanism includes a corresponding control circuit to facilitate switching control. These control circuits can be implemented manually or automatically. In the case of pad-mounted transformer tap changers, manual operation is commonly employed.
During the switching process, the tap changer connects or disconnects different taps via a contactor. When the tap changer is connected to a specific tap, the corresponding winding engages in power conversion, thereby adjusting the output voltage.
The tap changer's connection mode typically involves switching between star and delta connections, or vice versa. This switching alters the configuration of the transformer's windings, consequently changing the quantity and magnitude of the output voltage.
During operation, it's crucial to consider the rated current and rated voltage of the tap changer to ensure the transformer operates normally and avoids overloading.
By employing the principles outlined above, the tap changer can effectively modify the transformer's output voltage to accommodate varying load requirements, thereby enhancing the flexibility and adaptability of the transformer.
Types of transformer tap changer
There are two main types of transformer tap changers: the non-excitation tap changer, also known as the off-load tap changer, and the on-load tap changer.
Non-excitation Tap Changer (Off-load Tap Changer):
The non-excitation tap changer regulates voltage by changing the tap on the high-voltage side of the transformer. It adjusts the turns ratio of the winding when both the primary and secondary sides of the transformer are disconnected from the power supply. This type of tap changer is typically operated when the transformer is not under load.
On-load Tap Changer:
The on-load tap changer adjusts the tap of the transformer winding to regulate voltage while the transformer is under load. Unlike the non-excitation tap changer, it changes the number of high-voltage turns without interrupting the load current. This tap changer allows for voltage regulation without disrupting the power supply to connected equipment.
Why does a transformer need tap changer?
As the input voltage from the grid fluctuates and the load connected to its secondary side changes, the transformer requires a tap changer to maintain a stable output voltage level.
- Grid voltage fluctuations: Variations in the voltage supplied by the grid impact the secondary voltage of the transformer. If the grid voltage increases or decreases, the transformer must adjust its output voltage accordingly to ensure the proper operation of the electrical equipment connected to its secondary side.
- Load changes: Alterations in the electrical load connected to the secondary side of the transformer can also influence its output voltage. For instance, shifts in load size or power factor may lead to fluctuations in the secondary voltage. To maintain consistent voltage levels, the transformer needs to adjust its output voltage as the load changes.
By utilizing a voltage regulating switch, the transformer can adapt its output voltage as necessary to compensate for grid voltage fluctuations and load changes, ensuring the stable and reliable operation of its secondary side electrical equipment. This capability is crucial for maintaining the stability and security of the power grid and supporting the uninterrupted operation of the power system.
Related Products
Related Article
Guide to Pad Mounted Transformer Fuse
This article will delve into pad-mounted transformer fuses, exploring what fuses are and how they function. We will discuss the types of fuses required for pad-mounted transformers and guide on selecting the appropriate fuse for your specific needs. Furthermore, readers will gain insights into the functions and advantages of fuses used in pad-mounted transformers.
Guide to Types of Low-Voltage Bushings for Pad-Mounted Transformers
In our previous discussion, we delved into the various types of Pad Mounted Transformer HV Bushings. Today, Daelim Transformer is here to guide you through understanding the types of Pad Mounted Transformer LV Bushings.
Guide to Types of High-Voltage Bushings for Pad-Mounted Transformers
Are you uncertain about which high-voltage bushing your pad-mounted transformer requires? Let our guide to pad-mounted transformer HV bushings enlighten you on the various types and their applications. Pad mounted transformers come in two primary types: dead front and live front. Each type corresponds to different high voltage bushing designs: dead front bushing and live front bushing.
Basic Guide to Block Chain Transformers
Block chain operations are primarily concentrated in North America. Commonly used transformer types in these operations include pad-mounted transformers, three-phase power transformers, and HV substation transformers. Let's delve into each type in detail.
Comprehensive Guide to Pad-Mounted Transformers
The pad-mounted transformer is a prevalent and widely used type of distribution transformer in the Americas. Its operating principle is akin to other transformer types, utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction to either decrease or amplify the voltage level. Below, we will delve into the structure, accessories, design and production standards, and application scenarios of the pad-mounted transformer.
What is electrostatic interference in Transformers
Transformer electrostatic shielding minimizes electrical noise and interference by blocking capacitive coupling between windings. It enhances transformer performance, ensures signal clarity, and protects sensitive electronics. Common shielding materials include copper, aluminum, and conductive coatings, chosen based on performance and cost. Proper placement, grounding, and material selection are crucial for effective shielding. This technique is widely used in medical, aerospace, and defense applications to ensure stable electrical performance and prevent disruptions.
















