How to Build a Transformer

Electric transformers are essential components in modern power systems, enabling the efficient distribution of electricity by converting high-voltage electricity into lower-voltage electricity suitable for everyday use. The build process of transformers involves several meticulous steps, each critical to ensuring their reliability, performance, and safety.
Step-by-Step Guide to Build Transformer
1. Design and Planning
Before building a transformer, engineers meticulously design transformers based on specific customer requirements and technical parameters. Factors such as rated load, input/output voltage levels, and insulation requirements are carefully considered. Advanced simulations and calculations are conducted to validate the design's feasibility and efficiency. Comprehensive technical documents and drawings are prepared to guide subsequent manufacturing stages.
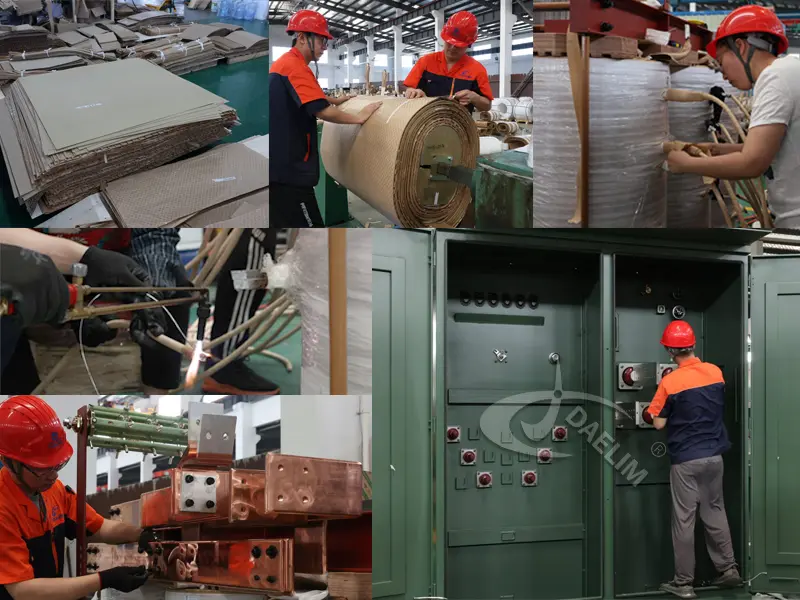
2. Material Preparation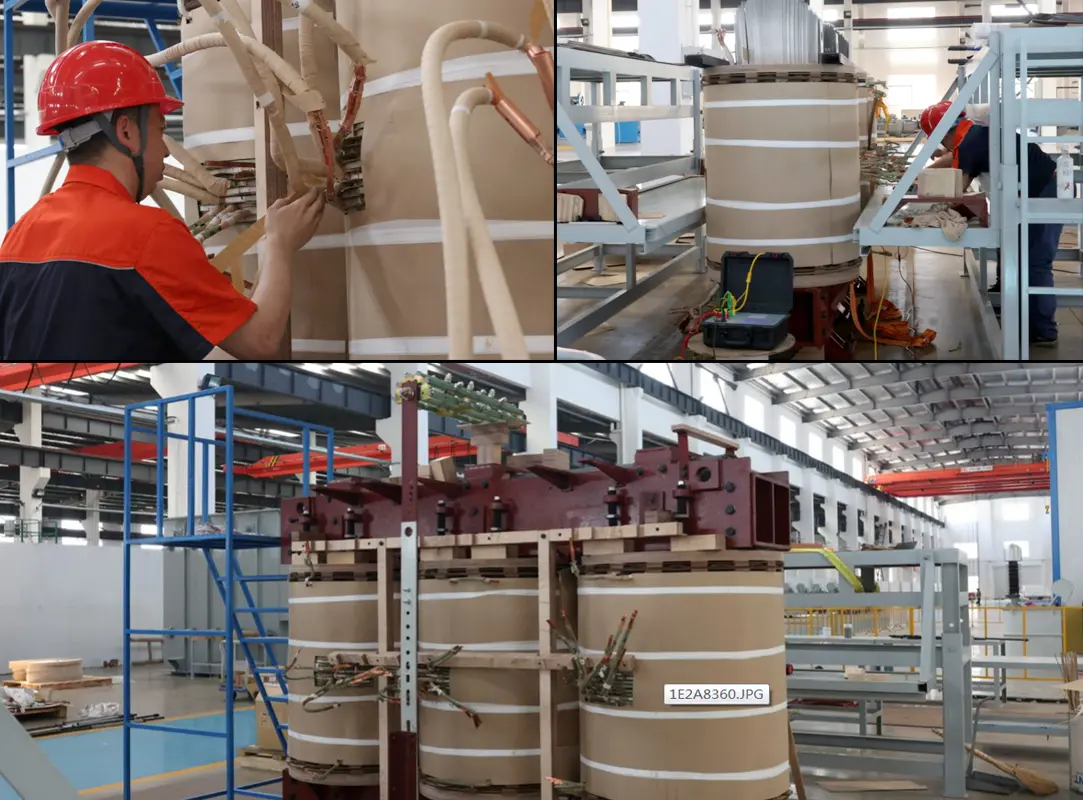
The building process commences with the meticulous preparation of materials essential for transformer construction. Key materials include silicon steel sheets, insulating materials, wires, insulating glue, and protective paints. Each batch of materials undergoes rigorous screening and testing to ensure compliance with national standards and performance requirements. High-quality materials are crucial for achieving optimal transformer performance and longevity.
3. Cutting and Assembly
Central to transformer assembly is the precise cutting and assembly of silicon steel sheets according to design specifications. Precision cutting tools and equipment are employed to ensure exact dimensions and shapes, crucial for efficient magnetic flux within the transformer core. Assembled silicon steel sheets are meticulously configured into iron cores, ensuring adherence to geometric and size requirements specified in the design.
4. Winding and Insulation Treatment
Winding, a critical component of transformer construction, involves carefully winding copper wires onto the assembled iron core. Each winding layer is meticulously insulated with epoxy-coated insulation paper to prevent electrical contact and ensure robust insulation integrity. This process demands precise execution to maintain winding quality, efficiency, and minimal energy loss.
5. Assembly and Welding
Following the completion of core and winding components, transformers undergo comprehensive assembly and welding processes. Skilled workers meticulously assemble all components according to design specifications, ensuring secure and reliable connections without any potential for leakage or short circuits. Concurrently, essential components such as cooling systems and oil tanks are installed to facilitate optimal transformer performance.
6. Insulation Testing and Debugging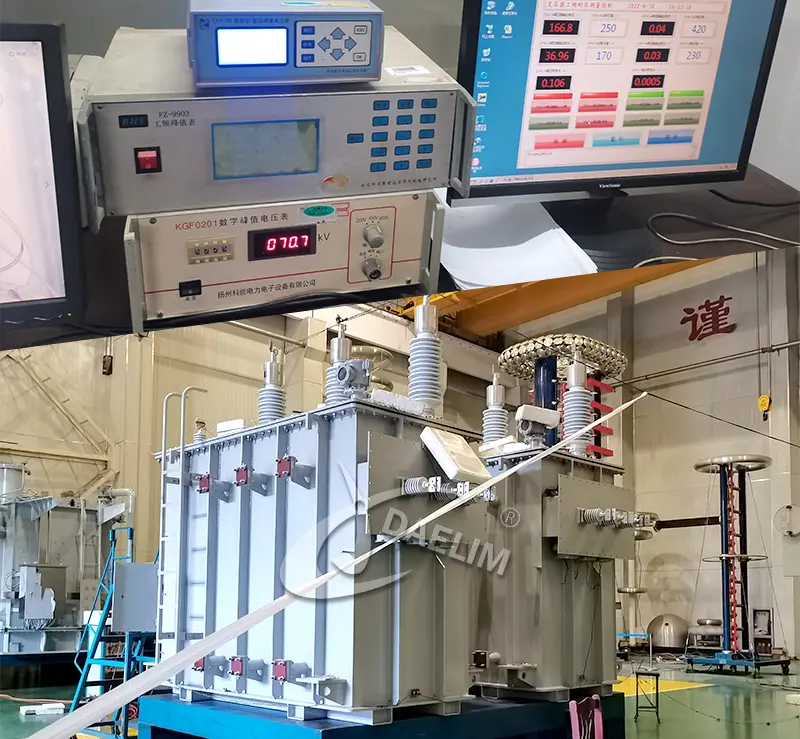
Post-assembly, transformers undergo rigorous insulation testing and debugging procedures to guarantee operational safety and reliability. Various tests, including insulation resistance measurement, dielectric loss assessment, and short-circuit impedance testing, validate transformer performance parameters. Thorough debugging ensures that any potential operational issues are identified and resolved before deployment.
Reading more: How to test a power transformer?
7. Additional Process Links
Beyond core manufacturing stages, supplementary processes such as oil immersion treatment and drying are critical. Oil immersion enhances transformer insulation and heat dissipation capabilities, while drying treatments prevent moisture accumulation that could compromise transformer performance over time.
Try for free: Steps In Power Transformer Manufacturing Process
Conclusion
The intricate process of building transformers encompasses a series of meticulously orchestrated steps, from initial design and material preparation to final testing and quality assurance. Each stage demands precision, expertise, and adherence to stringent quality standards to produce transformers of exceptional reliability and performance. As a pivotal component in modern power infrastructure, transformers manufactured through rigorous processes ensure efficient electricity distribution and contribute to the advancement of the power industry.
For further insights into building transformers and related topics, visit Daelim Transformer to discover our comprehensive range of high-quality and certified transformer solutions.
Related Products
Related Article
Temperature Protection and Maintenance for Transformers
Transformers require precise temperature protection, monitoring insulation grades, and appropriate oil types. Dry-type transformers trip at 130°C, oil-immersed at 90°C. In cold climates, FR3 fluid is recommended for its effective performance at -50°C.
Advantages of Transformer Yyn0 Vector Group
The Yyn0 vector group transformer offers distinct advantages in suppressing high-order harmonic currents and managing low-voltage single-phase ground short-circuit faults. However, it does have limitations regarding the handling of single-phase unbalanced loads, where the Dyn11 connection demonstrates superior performance. These characteristics should be carefully considered when selecting the appropriate transformer connection for specific applications to optimize performance and reliability.
Impact of Operating Temperature on Transformers
Maintaining an optimal operating temperature is crucial for the longevity and reliability of transformers. Excessive temperatures accelerate the aging process of the winding insulation, leading to a significant reduction in service life. Ensuring that the hottest point temperature remains within safe limits can help in maximizing the operational lifespan of transformers and maintaining their performance. For long-term efficiency and reliability, it is essential to monitor and control the operating temperature of transformers.
Transformer Drying Methods and Procedures
The article outlines transformer drying methods: oil tank iron loss, zero-sequence current, and vacuum dehumidification, emphasizing controlled heating and moisture removal for enhanced insulation reliability.
Transformer Oil Aging, Regeneration, and Purification
Effective management of transformer oil ensures prolonged equipment lifespan and reliable performance in electrical applications.
Technical Requirements for Transformer Installation
The article outlines critical technical requirements for transformer installation, covering support, grounding, cable management, safety measures, and fan operation to ensure safe and efficient electrical system performance.









