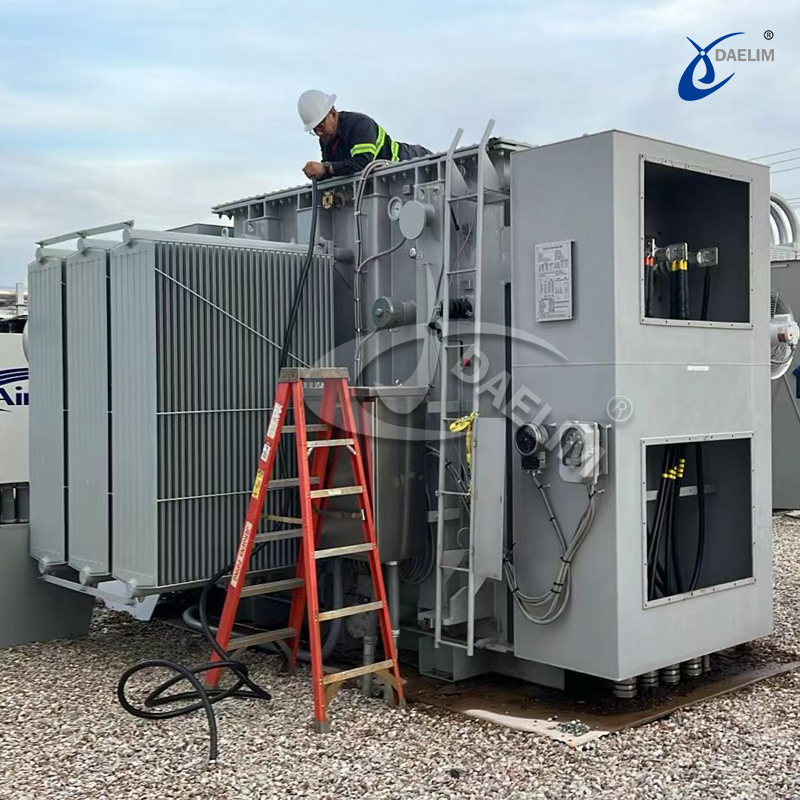
Everything You Need to Know About Transformer Dimensions
Knowing the transformer dimensions is important when making selections, installing, or maintaining a transformer for efficient and safe operation. Proper knowledge about size and space requirements is directly correlated with installation feasibility, operating efficiency, and safety standards.
This guide discusses the most crucial transformer sizes and provides clear information to engineers, technicians, facility managers, and utility company employees. Armed with this knowledge of transformer dimensions, they will ensure transformers fit well in their spaces, work better, and are safe in the facility.
Contact Daelim Transformer
Daelim Transformer's three-phase substation transformers are designed for high voltages up to 44 kV and ratings of up to 20 MVA, compliant with global standards such as ANSI/IEEE C57, CSA C88, IEC 60076, and AS. These transformers are equipped with monitoring system accessories and feature components from internationally renowned brands like ABB, Copper, and Qualitrol.

At our facility in Houston, we have hundreds of transformers in stock, including pad-mounted transformers ranging from 300 kVA to 3000 kVA, with voltage levels of 12.47, 13.2, 13.8, 24.94, and 34.5 kV. We also offer single-phase transformers with capacities from 50 to 175 kVA. There's no need to wait—immediate shipment is available!

Daelim Transformer offers a complete line of oil-immersed transformers that meet current applicable standards, including IEC, IEEE, ANSI, CSA, NEMA, AS/NZS, and GOST. Our high-voltage power transformers are available for voltages up to 230 kV and ratings up to 300 MVA. We have successfully supplied hundreds of high-voltage power transformers across America.
Standard Transformer Dimensions by Type and Power Rating
When selecting a transformer, you should know its size and where it is applied. Let us discuss several common types of transformers in their standard sizes so that the reader can understand how each type fits into different spaces and tasks.
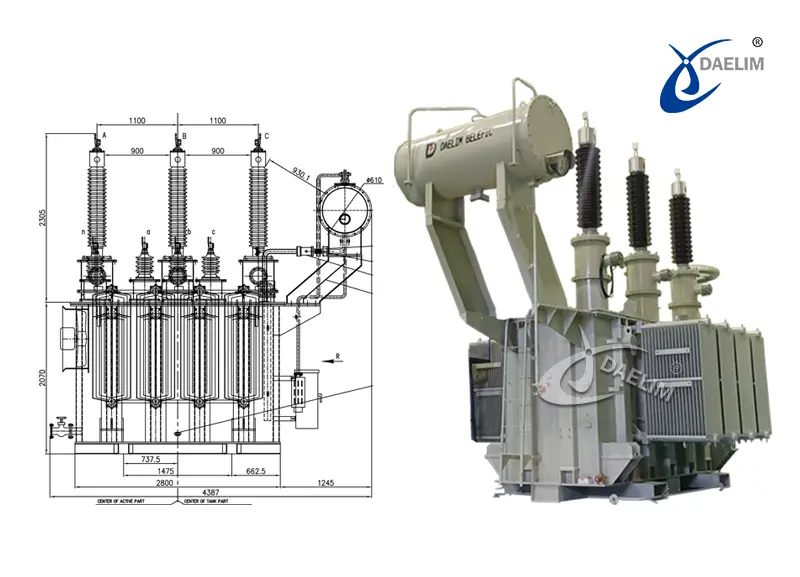
Physical Sizes of Transformers
Three-phase, pad-mounted distribution transformers with separable insulated high-voltage connectors
| Rated kV. A Capacity | Type of Feed | Transformer Maximum BIL, kV | Width, mm |
| 75, 150 | Radial | 95 | 1280 |
| 75, 150, 225, 300 | Loop | 95 | 1480 |
| 75, 150, 225, 300, 500 | Radial | 125 | 1480 |
| 75, 150, 225, 300, 500 | Loop | 125 | 1480 |
| 750, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000 | Radial | 125 | 1730 |
| 750, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000 | Loop | 125 | 1730 |
Source: Canadian Standards Associations
Medium Voltage Transformer
- Voltage Range: Typically from 1kV to 35kV.
- Applications: Primarily used for medium-sized power distribution networks, electrical power users, power plants, and substations.
- Common Voltages: 6kV, 10kV, 20kV, 35kV, etc.
- Dimensions:
- 500kVA: 1.5 m (L) x 0.9 m (W) x 1.2 m (H); weight around 1,800 kg
- 1,500 kVA: 2 m (L) x 1 m (W) x 1.5 m (H); weight around 3,800 kg
- 3,000 kVA: 2.2 m (L) x 1.2 m (W) x 1.8 m (H); weight around 5,200 kg
High Voltage Transformer
- Voltage Range: Typically from 35kV to 220kV.

- Applications: Used for power transmission over long distances, such as in high-voltage transmission lines, power stations, and substations.
- Common Voltages: 66kV, 110kV, 220kV, etc.
- Dimensions:
- 5,000 kVA: 4 m (L) x 2.5 m (W) x 3 m (H); weight around 20,000 kg.
- 10,000 kVA: 5 m (L) x 3 m (W) x 3.5 m (H); weight around 35,000 kg.
- 25,000 kVA: 6.5 m (L) x 4 m (W) x 4 m (H); weight around 65,000 kg.
Ultra High Voltage Transformer
- Voltage Range: This often exceeds 220kV; however, it may be as high as 1000kV.
- Applications: Transmission of the power over long distance in ultra high voltage transmission, reducing power losses while in transmission.
- Common voltages: 330kV, 500kV, 750kv, 1000kV, etc.
- Dimensions:
- 500,000 kVA: Approximately 8 m (L) x 4.5 m (W) x 5 m (H); weight around 280,000 kg.
- 1,000,000 kVA: Approximately 12 m (L) x 6 m (W) x 6 m (H); weight around 450,000 kg.
- 1,500,000 kVA: Approximately 15 m (L) x 7.5 m (W) x 7 m (H); weight around 700,000 kg.
See transformer types for your needs.
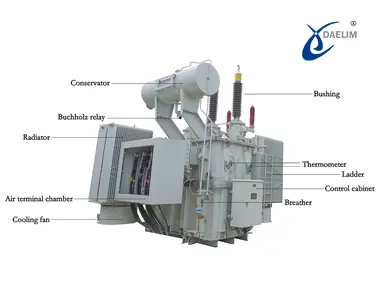
Key Components of Transformer Dimensions
Every transformer part is designed to a certain dimension that impacts the transformer's performance. If you know the main parts of transformer dimensions, you can understand why transformers are built this way and why specific dimensions are required, especially in industrial applications.
Core Dimensions
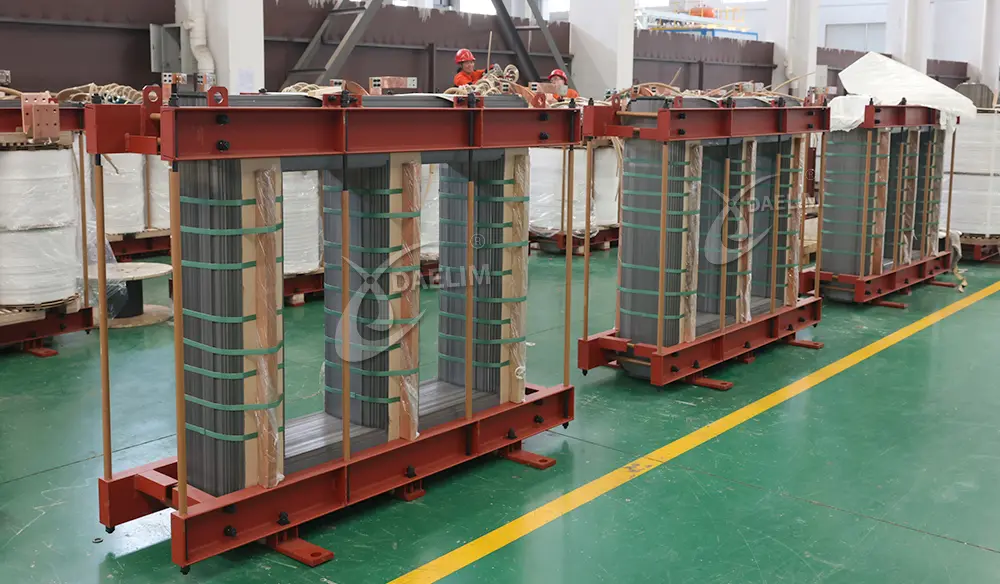

The core is the heart of the transformer. It is metallic and helps transform high voltage to low voltage or vice versa. The size of the core is directly proportional to the amount of electricity that a transformer can handle. Generally, transformer cores are relatively more important for higher voltage transformation, which in most cases means they are sturdier and more effective.
The transformer core cannot be too small since that would limit the maximum power that can be allowed in the transformer and make it less efficient. Again, if the core were too big, the transformer would be too heavy and occupy much space. Thus, its dimensions are the main trade-off between performance and space.
Winding Dimensions
The coils of wire wrap around the core. Their size and thickness determine whether the transformer has to bear higher or lower currents.
Larger windings force the transformer to carry larger currents but tend to increase heat dissipation. Thin or small windings will heat up and deteriorate the transformer's performance or even destroy it.
Every transformer capacity should have appropriate windings of the right thickness and material. High-capacity transformers, such as those in huge factories, require thicker windings to carry large volumes of power while cooling down safely.
Tank Dimensions
 The outer casing is referred to as the tank, which protects the inner parts of the transformer and holds the cooling oil or air. The size of the tank will depend on the transformer's power rating. In larger industrial transformers, a larger tank is necessary to accommodate the core and windings safely and provide room for cooling.
The outer casing is referred to as the tank, which protects the inner parts of the transformer and holds the cooling oil or air. The size of the tank will depend on the transformer's power rating. In larger industrial transformers, a larger tank is necessary to accommodate the core and windings safely and provide room for cooling.
The high-power transformers are quite larger and heavier, which would make them even better protected. Industrial transformers need enough space in the tank, especially for proper oil or air cooling under very hot working conditions, if they are to possess long-lasting durability.
Cooling System Dimensions
An important part of the industrial transformer's usage is its cooling system, which allows it to manage the loads on high power and their heat. Size, in general, within the cooling system mostly relates to radiators or fans and circulation systems in the oil. This is essentially determining the total size of the transformer.
A certain size must correspond to the transformer's capacity so that no overheating will occur.
- Radiator Size Requirements: Radiators work like heat exchangers in the case of a transformer. The sizes would depend on the transformer power rating. The height for medium-power transformers is 4-6 feet. In high power, the radiator might be around 10 feet in height, and in some transformers, it extends several feet more to widen for proper heat dissipation. Larger radiators provide ample cooling to the system, but it will be rather significant additions to the transformer's footprint.
- Fan Size Requirements: Fans are added to a transformer to enhance cooling radiator capacity. Transformers as small as 1 foot by 2 feet may employ fans that are up to 4 feet in width for cooling wider areas of the radiator where a high-power transformer requires fans. Fans will further increase the width and length when attached on either the top sides of the setup.
- Oil Circulation System Size Requirements: High-capacity transformer oil circulation systems carry heat away from the core and windings; pumps, piping, and oil tanks may be included. Low-to-medium-capacity transformers only require simple oil-flow channels, while larger types need external tanks and pumps that can protrude feet in every direction and add a few pounds in weight plus volume to the unit.
It is very important to have the appropriate-sized cooling system to ensure that the transformer is safe and efficient. Cooling components should be greater and stronger in high-capacity transformers since less cooling can cause overheating and, thus, system breakdown.
Determining the Right Transformer Dimensions for Your Needs
Proper transformer sizing requires the consideration of what power the transformer must serve, where it will be, and how it is supposed to be used. Here are the simple steps and important things to consider:
Calculate Dimensions
Given the Load, Determine the power load that your transformer must feed. The load rating is usually a Power Capacity rating in kilovolt-amps (kVA) or mega-volt-amps (MVA).
Higher load ratings mean the transformer will need larger core and winding sizes and a more extensive cooling system. So, if your site has high power demands, you’ll need a bigger transformer with ample room for cooling systems like radiators and fans.
Consider Location and Space
Identify the location to which you are moving the transformer and the space you will have available. Indoor transformers are usually less weatherproof than outdoor transformers but would generally take more space because of ventilation. For most industries, clearances of 3-5 feet are used when installing transformers for easier access and safer people.
Match Dimensions to Industry Standards
Transformer dimensions need to meet industry standards for safety and efficiency. Two prominent standards for dimensioning in the world of transformers are the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
IEC standards are widely applied worldwide and make detailed recommendations for core size, cooling space, and safety clearances. ANSI standards, commonly followed in North America, require size, grounding, and installation spaces for different types of transformers.
More resource:
Pad Mounted Transformer CSA C227.4 National Standard of Canada
CSA C88 Standard For Power Transformers
CSA C802 For Minimum Efficiency Values For Power Transformers
CSA C227.3 For Single Phase Pad Mounted Distribution Transformer
Three Phase Live Front Pad Mounted Transformers Under CSA C227.5
Follow Space Allocation Guidelines
To ensure your transformer fits safely and functions well, follow the space guidelines given by IEC or ANSI. For example, if the IEC standard suggests a minimum clearance for cooling or safety, you’ll want to ensure your transformer’s surroundings allow for this space. Without proper spacing, transformers may overheat, especially if cooling parts like radiators and fans don’t have enough room to work effectively.
All these steps will help you choose the right size transformer that suits your needs, is appropriate for space, meets power demands, and adheres to safety rules.
Conclusion
Choosing the right transformer dimensions size is key for safety, performance, and efficiency in industrial settings. By understanding your load requirements, space constraints, and industry standards (like IEC or ANSI), you can select a transformer that meets your facility’s needs. Cooling, safety clearances, and core and winding dimensions all play a role in making the best choice.
Daelim offers transformer solutions tailored to these standards, ensuring quality and reliability. Ready to find the ideal transformer? Contact us for expert guidance and options built to meet your industry’s demands!
Related Products
Related Article
A Guide to Tier 2 Transformers
This article discusses the EU's Tier 2 Ecodesign Regulations aimed at reducing transformer energy losses. By enhancing design and materials, these regulations lower CO2 emissions and operating costs. DAELIM Transformer is highlighted as a leader in producing compliant, high-efficiency transformers that support sustainability and improved energy performance.
Ultimate Guide To Transformer Sizes and Ratings
Transformers come in a wide range of sizes and ratings, and the specific requirements of the application will determine the appropriate size and rating for a particular transformer. It is important to choose a transformer that is specifically designed and rated for the required voltage, current, power, frequency, and temperature levels.
Understanding Types of Transformer Winding and Their Applications
This article explains the different types of transformer windings used in core-type and shell-type transformers. It covers helical, cylindrical, disc, and sandwich windings, detailing their unique structures, cooling benefits, and applications. Core-type transformers use windings like helical and cylindrical to manage varying voltages and currents, while shell-type transformers employ sandwich windings for improved efficiency and insulation. The article highlights the importance of winding design in optimizing transformer performance, cooling, and mechanical strength for various industrial applications.
What different materials are used in a Transformer?
Transformers use a variety of materials to ensure efficient operation and performance. Copper is commonly used for windings due to its excellent conductivity and ductility, while aluminum is a cost-effective alternative. Transformer cores are typically made from silicon steel for high flux density, with materials like amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys offering enhanced efficiency. Transformer oil, such as mineral oil and vegetable (FR3) oils, aids in heat dissipation. Additionally, transformer tanks are often made from low carbon or structural steel, and insulation is typically provided by Kraft paper. These materials work together to enhance transformer efficiency, safety, and longevity.
How Transformer Components Function Together to Control & Deliver Electricity
This article provides an overview of the key components of transformers and how they work together. It discusses the functions of transformer windings, cores, insulating materials, and transformer oil, as well as the roles of cooling tubes, tanks, and safety features. Overall, these components ensure effective voltage regulation and safe electricity delivery.
12+ FAQ Guide on Transformer Ratings
A power transformer rating is the maximum amount of electricity that it can safely and reliably transform. In most cases, this is always stated in kVA.