What different materials are used in a Transformer?

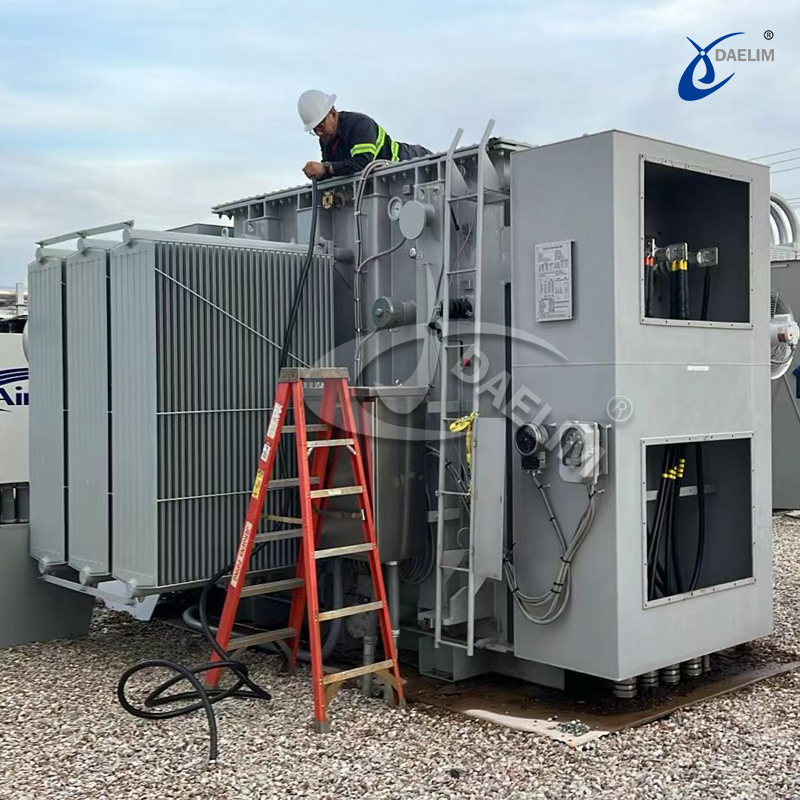
Electrical transformers are essential components of our modern electricity supply systems. They regulate electricity for our residential and industrial installations. To regulate that, their capacity ranges from 15 kVA to 500MVA.
With such a huge difference in the capacity, each transformer needs a different material to achieve high efficiency. This article brings you an insight on transformer material. Understanding why some special materials are required for transformer parts.
Contact Daelim Transformer
ECO design transformer(Tier 2) complies with the latest energy efficiency standards of the European Union, and has silicon steel core and amorphous alloy core transformers. Designed and produced according to IEC and BS standards, it is energy-saving, environmentally friendly and highly efficient.

Daelim Transformer offers a complete line of oil-immersed transformers that meet current applicable standards, including IEC, IEEE, ANSI, CSA, NEMA, AS/NZS, and GOST. Our high-voltage power transformers are available for voltages up to 230 kV and ratings up to 300 MVA. We have successfully supplied hundreds of high-voltage power transformers across America.

Daelim is a respected manufacturer providing UL/cUL and CSA pad-mounted transformers. Offer single-phase and 3-phase options, 3-phase transformers featuring up to 44kV voltage and ranging from 75kVA to 10,000kVA in power. Single phase pad mounted transformer with high voltage up to 34.5 kV and ratings up to 250kVA.
Different Transformer Parts and Their Materials
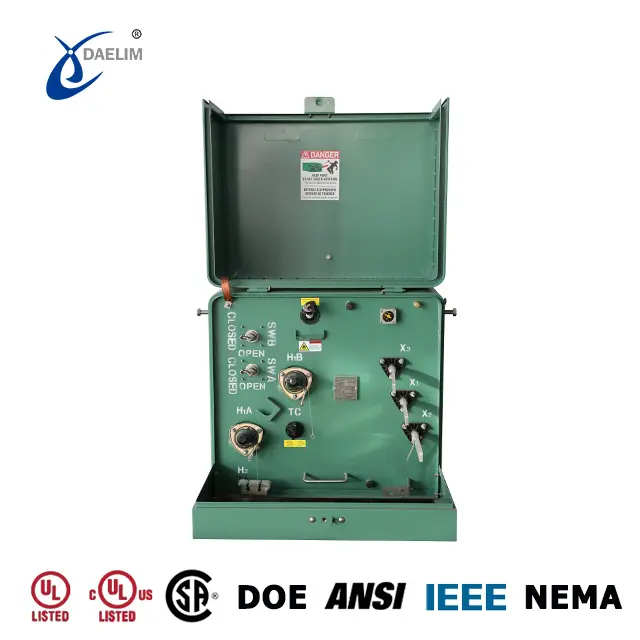
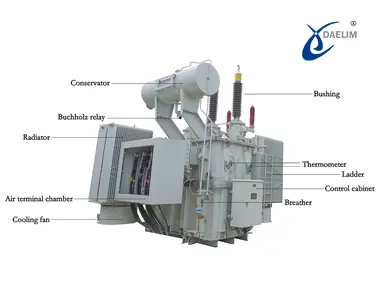
There are 12 different components in a transformer that work coherently to regulate and deliver electricity. As the core task of all transformer components is to help regulate electricity, material will play an important role here because of the electrical conductivity, which is a material property.
Transformer Winding
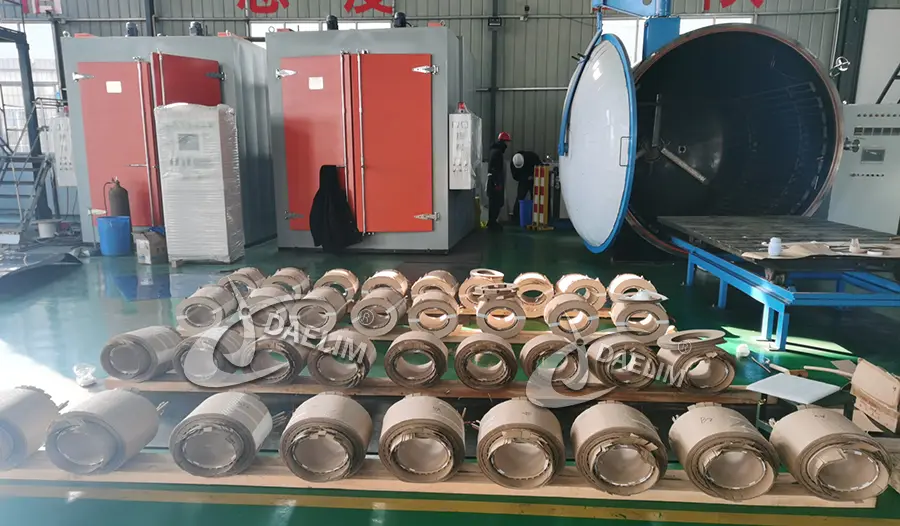

Transformer windings are the main components of any transformer with each single-phase transformer having minimum two windings. A primary winding that gets in input and a secondary winding that delivers the output. The number of turns in each winding is what determines the voltage regulation.
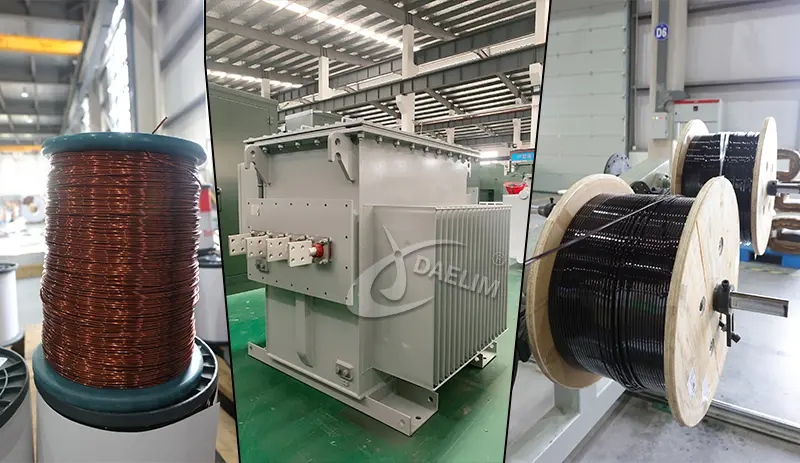
Copper is the most commonly used transformer material for high-quality transformer windings, primarily due to the working principle of the winding. The electric current flowing in primary winding develops an electromagnetic induction in the core of the transformer.
The core transfers the electromagnetic induction to the secondary winding where secondary current and voltage is developed. How much electric current and voltage developed in secondary winding by the magnetic induction depends on its number of turns.
As this entire process depends on the ability of winding to develop and absorb electromagnetic flux. The use of material with excellent electrical conductivity is very important here. Copper being an excellent conductor of electricity produces and absorbs electromagnetic flux quite efficiently.
Copper ductility is another mechanical property why it is recommended as a transformer winding material. Winding is done by winding copper wire around the core in multiple turns. So more the ductility of the material is easy to wind it at core.
Other materials properties including corrosion resistance, mealiability, and chemical stability in a high temperature environment make copper an excellent choice for transformer winding. One disadvantage of copper is the material cost. Among all the conductive materials used in industry in masses, copper is the most expensive material.
Due to the high cost of material associated with copper, an alternate transformer material called aluminum is also used extensively for transformer winding. Aluminum is also a good conductor of electricity and is a highly ductile material, so easy to wind on the transformer core. Aluminum is a light weight material and has very good corrosion resistance and high thermal stability.
Transformer Core
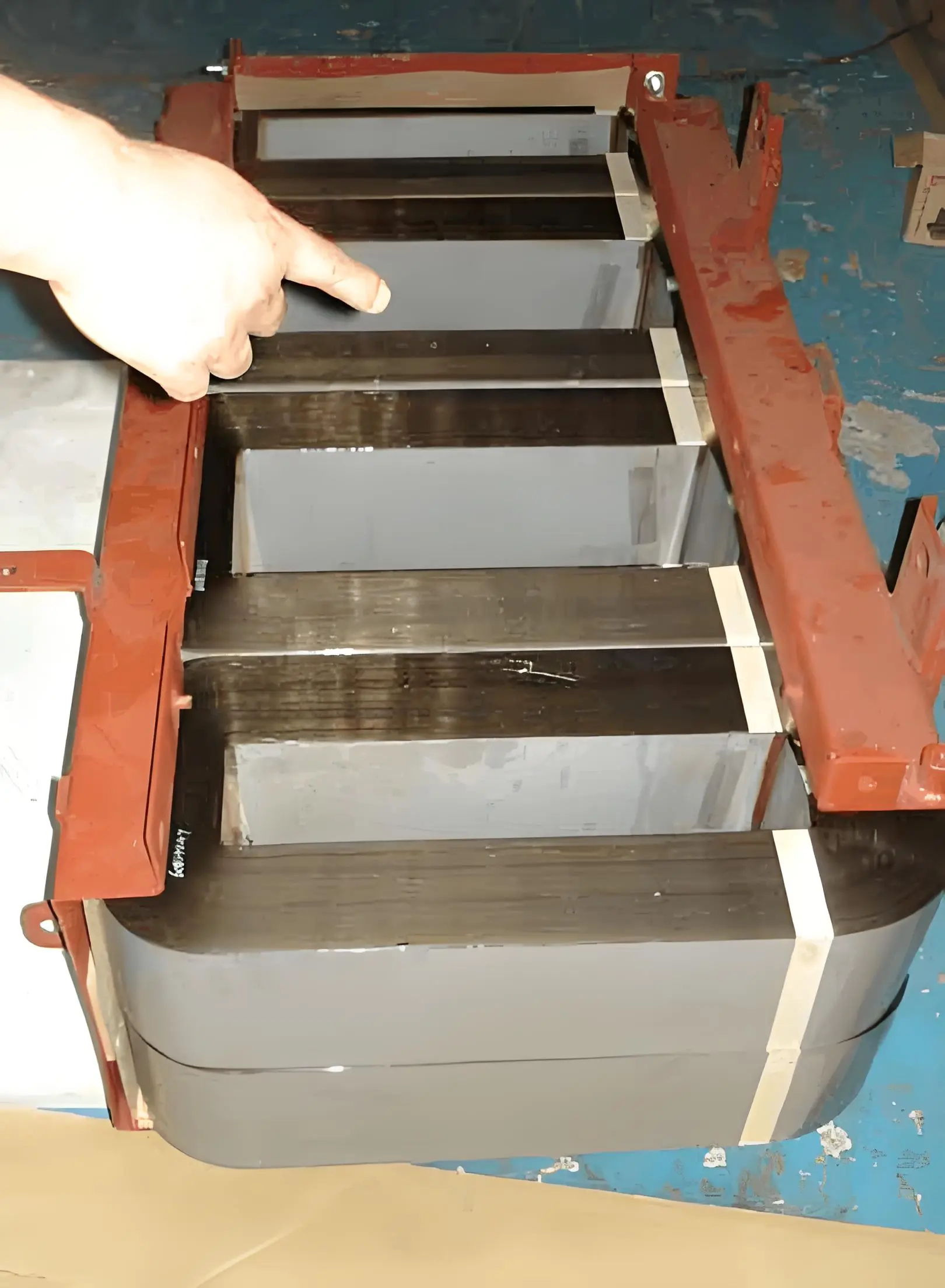 Transformer core plays an important role in regulating electricity between grid stations and consumer installations. Core helps efficiently transfer electromagnetic flux from primary winding to secondary winding.
Transformer core plays an important role in regulating electricity between grid stations and consumer installations. Core helps efficiently transfer electromagnetic flux from primary winding to secondary winding.
A cold rolled sheet of silicon steel is the most widely used transformer material for electrical transformer cores. This steel type is specifically used for manufacturing core for power transformer and distribution transformers. Silicon steel enables highly efficient electromagnetic flux induction in the transformer core resulting in increased transformer performance.
There is another advantage of steel and it is steel density, due to high density and electrical conductivity, steel offers high flux density. Silicon steel also minimizes the energy loss for each magnetization cycle during transformer working.
Amorphous Alloy is another material used in the manufacturing of transformer cores. This material is especially used for manufacturing of distribution type transformers and instrumented transformers.
Main reason why this material is used is that it offers very little core losses as it induces very less eddy current losses due to its excellent electrical conductivity. It is due to this reason that it offers high efficiency and eco friendly application.
More resource: A Complete Overview of Amorphous Metal Transformers
Nanocrystalline alloy is another transformer material that is being used for dedicated transformers. These transformers include renewable energy transformers and high efficiency transformers. These Nanocrystalline alloys are best for delivering very high thermal stability and have very high frequency response. Core made from this material also offers lower core losses and good saturation flux density.
Transformer oil

In a transformer, oil is crucial for heat dissipation that is produced by the transformer winding. Oil works as a medium of heat transfer from transformer winding to the transformer tank. Mineral oils are mostly used in transformers for this heat dissipation purpose. Among all mineral oils Paraffinic oil and Naphthenic oil are the two most used oils for transformers.
There are some specific properties that are needed to be considered when selecting oil for oil type transformers. Properties including electrical properties, chemical properties, and physical properties are considered during the selection process.
Paraffinic oil is obtained from a specific type of crude oil that has very low content of wax technically known as n-paraffin. It is due to this low wax content that this mineral oil has low pour point and high boiling point of 425 C. One disadvantage of this oil is its tendency to corrode which limits its use in high end and long lasting solutions.
Opposite to that of paraffinic oil, naphthenic oil obtained from crude oil that has high wax content. Due to this it has a high pour point as compared to paraffinic and has a higher boiling point of 530 C. This high wax content and specific base crude oil make naphthenic highly resistant to oxidation. One disadvantage of this oil is that the little oxidation that happens over time is not soluble in oil.
Both oils have excellents electrical properties like both are bad conductors of electricity. Both oils have high dielectric strength meaning that they have very low moisture content and need extremely high voltage to break the oil content. In any given situation, the minimum value of dielectric capacity is 30,000 Volts.
Transformer tank
 Transformer tank is one of the most important parts of a transformer as it contains all other important transformer parts. Transformer tanks help radiate heat safely into the environment and also help protect parts like winding and core from harmful environmental factors like moisture.
Transformer tank is one of the most important parts of a transformer as it contains all other important transformer parts. Transformer tanks help radiate heat safely into the environment and also help protect parts like winding and core from harmful environmental factors like moisture.
Considering the working of the transformer tank, materials like carbon steel specially low carbon steel are mostly used in their manufacturing. Some great advantages of using low carbon steel for tank manufacturing.
Low carbon steel is one of the most easily available materials for manufacturing. Its weldability and machinability make this material very easy to work with, thus reducing cost of manufacturing. Some disadvantages of using low carbon steel are that it has light magnetic properties and has very little resistance against rust and corrosion.
Structural steel is an excellent option to cover all disadvantages of low carbon steel. It offers no magnetic properties so it's an excellent option for transformer tank manufacturing. Its composition ensures high corrosion resistance, ensuring protection of the tank and all internal transformer parts from the external environment.
Structural steel is more expensive and difficult to manufacture when compared to low carbon steel but the quality it offers make it the best option for transformer tank manufacturing.
Transformer Insulation
In a transformer, winding that is done on the transformer core is insulated from the core using special insulating material. Each turn or layer of winding wire is also insulated from the other turn or layer using insulating material.
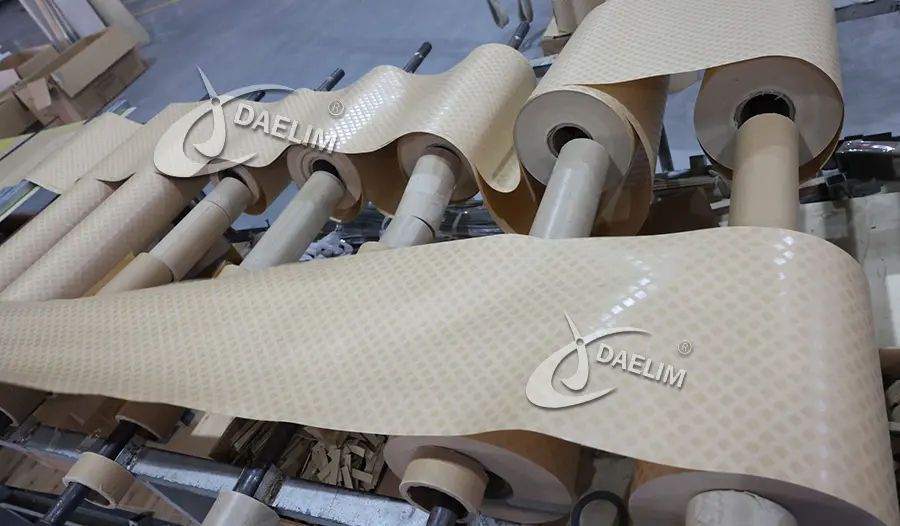

In oil type transformers this insulation material is special paper, more like a very thin cardboard that has some good heat resistance properties. Kraft paper is the most used one for this purpose. One sheet of paper when placed between core and winding or each winding layer provides a complete insulation and non-contact assembly of parts.
This paper can provide insulation but cannot resist all the heat produced by winding. To protect it from heat, it always remains dip in transformer oil.
Conclusion
Transformers rely on a diverse range of materials. Each material is selected for specific properties that enable the efficient regulation of electricity. Starting from copper windings to silicon steel cores to specialized oils to durable insulating papers. Each material has a unique role that contributes to the transformer overall performance, safety, and longevity.
Choosing the right materials ensures that transformers operate effectively. It ensures that it can withstand environmental challenges, ultimately supporting the stable and reliable electricity distribution needed in both residential and industrial settings.
Follow Up
To our loyal readers, hopefully we have written something that has helped you get an insight on what different transformer parts are made off. At DAELIM, we design, develop, and supply transformers of all types and sizes. Our inventory has but is not limited to power transformers, distribution transformers, and special transformers for renewable energy power plants.
We offer transformers made from various materials. Daelim Transformer have facilities in the United States and China. If you have any query on this topic or want to know any further, Contact Us and our dedicated team will get you through the process. If you have any query on this topic or want to know any further, Contact Us and our dedicated team will get you through the process.
Related Products
Related Article
How to Choose Transformer Supplier
Choosing the right transformer supplier is crucial for ensuring stable power supply and efficient operations. Start by identifying your specific transformer needs, researching potential suppliers, and evaluating their quality and reputation. Consider pricing, customer support, and delivery logistics. Ultimately, trust your instincts and maintain open communication to establish a strong partnership. Discover reliable solutions with Daelim for optimal energy usage.
A Guide to Tier 2 Transformers
This article discusses the EU's Tier 2 Ecodesign Regulations aimed at reducing transformer energy losses. By enhancing design and materials, these regulations lower CO2 emissions and operating costs. DAELIM Transformer is highlighted as a leader in producing compliant, high-efficiency transformers that support sustainability and improved energy performance.
How Transformer Components Function Together to Control & Deliver Electricity
This article provides an overview of the key components of transformers and how they work together. It discusses the functions of transformer windings, cores, insulating materials, and transformer oil, as well as the roles of cooling tubes, tanks, and safety features. Overall, these components ensure effective voltage regulation and safe electricity delivery.
Why Is Transformer Oil Change Important?
This article emphasizes the importance of transformer oil changes for reliable transformer operation. Transformer oil provides insulation, cooling, and protection against moisture and oxidation. Regular replacements prevent moisture accumulation, oxidation, and particle contamination, ensuring safety and efficiency. Key steps for an oil change are outlined, highlighting the benefits of routine maintenance, including enhanced reliability, extended lifespan, and reduced operational risks.
Transformer Design: Step by Step Guide for Safety and Reliable Power Flow
This guide outlines the step-by-step process for designing transformers, covering key stages from requirement analysis to testing and production. It highlights the importance of adhering to relevant standards like IEEE, IEC, and ANSI, and emphasizes the selection of materials, winding design, cooling systems, and insulation for efficiency and safety. Proper mechanical design, protection devices, and thorough testing are critical for ensuring reliability and performance. The guide concludes with the importance of accurate documentation and continuous improvement in transformer design for long-term efficiency and durability.
Understanding Types of Transformer Winding and Their Applications
This article explains the different types of transformer windings used in core-type and shell-type transformers. It covers helical, cylindrical, disc, and sandwich windings, detailing their unique structures, cooling benefits, and applications. Core-type transformers use windings like helical and cylindrical to manage varying voltages and currents, while shell-type transformers employ sandwich windings for improved efficiency and insulation. The article highlights the importance of winding design in optimizing transformer performance, cooling, and mechanical strength for various industrial applications.